THERMIONIC EMISSION
Thermionic emission is the escape of electrons from a hot metal surface.
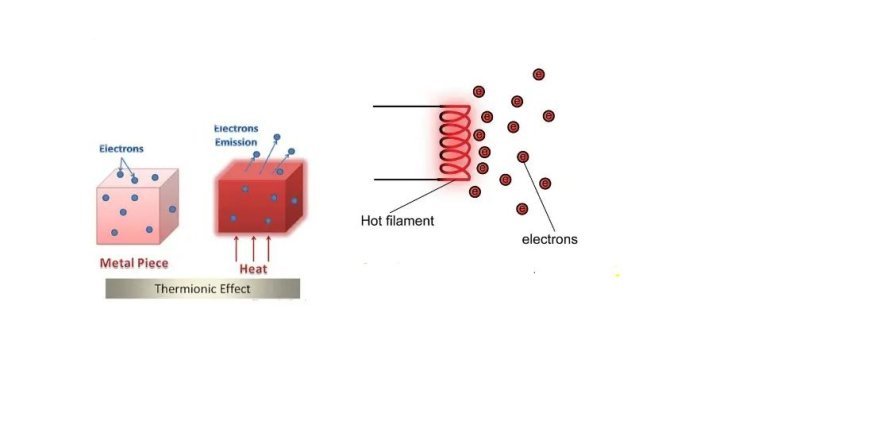
THERMIC EMISSION
- It is possible for ions to be released when heat is applied. This process is called thermoelectric emission.
- The words thermionic and emission are put together to make a single word that is used to talk about how heat can free tiny particles, especially electrons. This is the case because charged bearers were once thought of as thermions.
- It's also called the thermionic effect. In simpler terms, thermionic emission is when electrons are released from the surface of a metal when that metal is heated enough.
- Place of origin: Thomas Alva Edison came up with the idea of thermionic emission in the year 1883. Thomas was working on one of his projects and trying to figure out why the filament inside the bulb was breaking and turning black in different places.
Work Function
- In terms of the work function, this means that when the energy level is set to zero, the electrons have energy WF and the energy that comes from the outside is WE.
- The difference in energy between WE and WF demonstrates the metal's work function. This is the energy that is needed to free the electrons.
- The work function of the metal is shown by φ.
- For each metal, φ has a different number, and an electron volt is used to measure it. Most of the time, this is between 1 and 6 eV.
- After the charges are freed from the metal's surface, there are still an equal number of charges in the area where the electrons are released. These charges are the same size but have the opposite polarity.
Factors Affecting Thermionic Emission
- Based on the type of material, we are interested in the work role that material has. Valence electrons in the top shell are the main thing that determines what kind of metal it is. This is because these electrons will need heat energy from outside sources in order to be sent into space.
- Its work function is the smallest amount of energy that frees up the electrons.
- Metals have different work functions for different elements.
- Thermionic radiation and the surface area of a material behave in a way that is directly related to each other.
- As a result, there will be more electron release over a larger area. So, we can say that a metal with a large surface area will give off more electrons than a metal with the same properties but a smaller surface area.
- The temperature at the top of a metal affects the flow of thermionic waves through it.
- As a result, the rate of electron release will go up as the temperature of the object goes up.
- So, taking all three into account, we can say that for a metal to have better thermionic emission, it should have a low work function, a large surface area, and a high melting point.
What's Your Reaction?