SOIL EROSION CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES
Explore the causes and effects of soil erosion, including water and wind erosion, and learn about strategies for prevention and remediation.
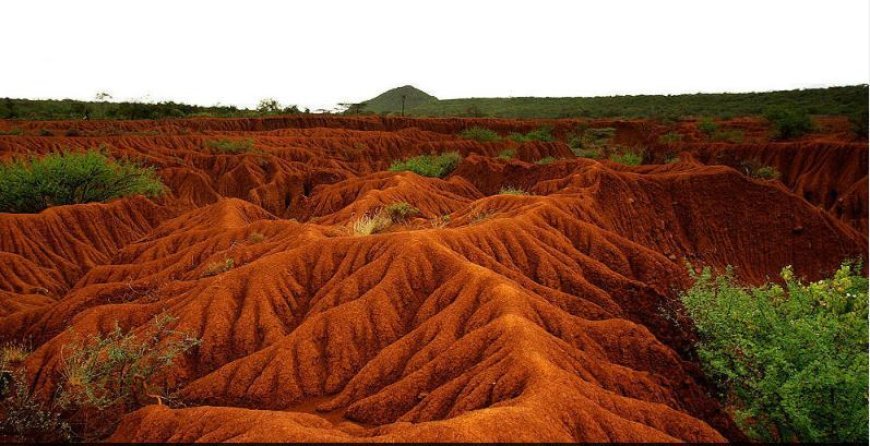

An In-depth Examination of Soil Erosion
- Soil erosion is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects ecosystems, biodiversity, and human societies worldwide.
- The cumulative degradation of topsoil, the uppermost layer of soil, has substantial consequences for agricultural productivity, water quality, and climate regulation.
- While soil erosion is an intrinsic reality, human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, and intensive agriculture have accelerated its occurrence, leading to disastrous outcomes for the environment and human well-being.
Geological Factors and Soil Erosion
- Geological factors significantly impact soil erosion, since several types of rocks and soil formations manifest varying levels of resistance to erosion.
- Regions with loose or sandy soil are more susceptible to erosion from wind and water, whereas areas with clay-rich soil may be more prone to landslides and mudstreams.
- Acquiring thorough knowledge of these geological components is crucial for the formulation of effective conservation strategies and the mitigation of soil erosion effects.
Implementation of Strategic Conservation Strategies
- Experimental studies have demonstrated that conservation tillage, a technique that reduces soil disturbance and preserves soil moisture, effectively reduces soil erosion.
- Cover crops, which offer soil protection and supply organic carbon, are an extra methodology that helps to maintain soil health.
- Terrecing, the methodical procedure of levelling the ground to reduce slope and flow, is highly effective in reducing soil erosion.
- Furthermore, regeneration and afforestation efforts have a role in the recovery of plant life, the avoidance of erosion, and the sustainable preservation of ecological balance.
Socio-economic factors
- The socio-economic implications of soil erosion are significant, particularly for communities that depend on agricultural production.
- The severe outcomes of soil degradation include displacement, poverty, and food insecurity.
- Moreover, metropolitan areas are particularly affected by soil erosion, as the accumulation of silt and pollution has detrimental consequences for water transmission systems and infrastructure.
- The economic consequences of soil erosion are significant, since estimates suggest that it causes billions of dollars in losses to the global economy each year.
Analysis of Education, Involvement of the Community, and Reformation of Policies
- In order to effectively address soil erosion, it is imperative to implement educational programs and actively engage the community.
- Disseminating information about the elements that contribute to and the outcomes of soil erosion might inspire individuals and communities to participate in preventative actions.
By implementing community-led initiatives, such as programs that prioritize soil conservation and the adoption of sustainable land use practices, it is possible to significantly mitigate the effects of soil erosion. - Furthermore, the execution of legislative changes and the provision of government aid are essential in promoting sustainable land use practices and successfully addressing the root causes of soil erosion.
What's Your Reaction?