CRITICAL FACTORS AFFECTING SLOPE STABILITY
Discover the key factors that influence slope stability, including geological, hydrological, and human-induced elements.
Critical Factors Affecting Slope Stability
- The comprehension of slope stability is of utmost importance in the prevention of landslides and the preservation of the structural soundness of both natural and controlled slopes.
- A multitude of interconnected elements may impact the stability of slopes, and they can be generally classified into environmental, geological, and human impacts.
- Climatic Variables
Meteorological variability
- Slope stability may be influenced by variations in precipitation intensity and duration.
- Accumulated precipitation may result in heightened soil saturation, therefore diminishing the soil's shear strength and rendering slopes more susceptible to collapse.
- The occurrence of temperature extremes, which include freeze-thaw cycles, may induce expansion and contraction of soil and rock, hence possibly heightening susceptibility to slope collapse.
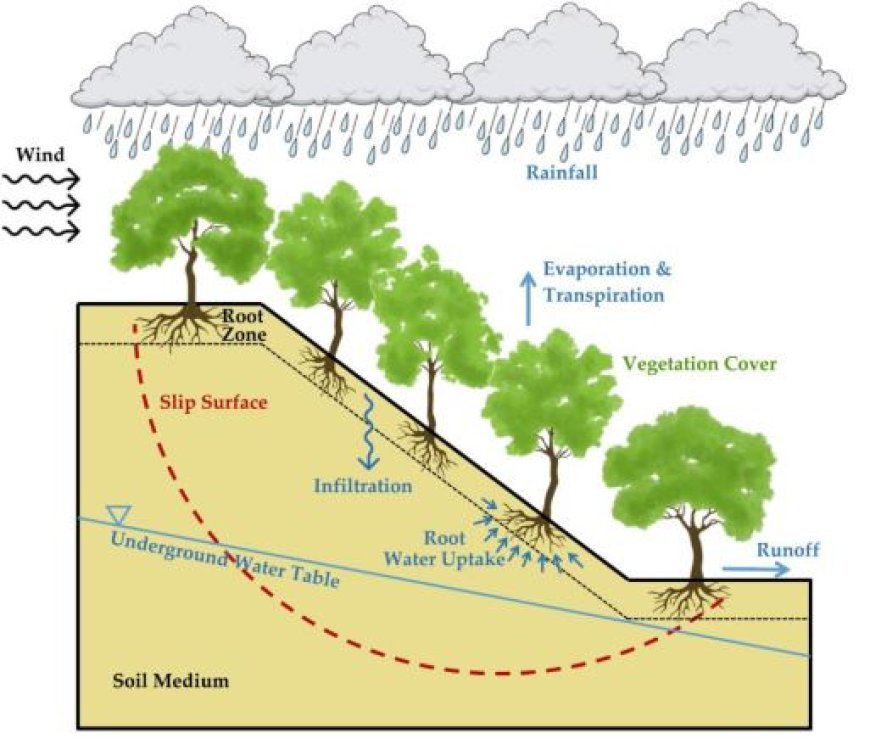
Botanical Cover
- Rood Structure: Vegetation is crucial in providing stability to slopes.
- Phytoliths' root systems facilitate the consolidation of soil particles, hence improving slope stability.
- Reversely, the act of clearing forests may result in heightened erosion and instability.
- Vegetation facilitates soil moisture management by absorbing water via its roots, therefore reducing the risk of excessive soil saturation that may result in slope instability.
Erosion and sedimentation processes
- Surface erosion refers to the process of topsoil being removed by wind or water, which tends to degrade slope surfaces and limit their stability.
- The process of sediment deposition at the foot of slopes has the potential to disrupt the natural equilibrium and ultimately result in heightened risks of collapse.
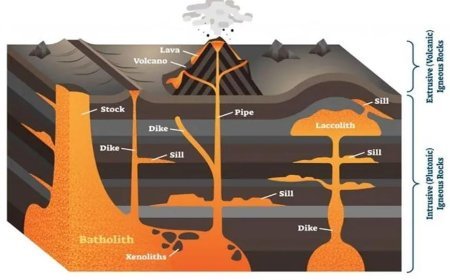
- Geological Factors
Terrain and Geological Characteristics
- Various soil types (clay, silt, and sand) exhibit different levels of cohesion and shear strength in terms of their texture and composition.
- For instance, clay soils have a higher water retention capacity and could become slippery when wet, while sandy soils may have lower cohesiveness but are more susceptible to erosion.
- Criteria for Rock Quality: The stability of slopes is influenced by the strength and integrity of the bedrock.
- Fractured or worn rocks might engender vulnerabilities that result in slope collapses.
Structural geology
- Geological strata's orientation and bedding characteristics influence the distribution of stresses over a slope.
- Sloping layers that incline towards the slope face might provide favorable circumstances for sliding.
- Geological structures may include natural faults or folds that might serve as possible failure surfaces, therefore increasing the vulnerability of slopes to instability.
Geochronological Evolution
- Historical documentation of previous landslides or ground movements may provide valuable information on the present stability of slopes and identify areas of particular danger.
- Effects of Hydrology
The Variations of the Water Table
- Variations in groundwater levels can have an impact on the soil's saturation and resistance. Elevated groundwater levels may increase the soil's mass and reduce its elastic properties.
Hydraulic surface flow
- Flow patterns of runoff: Surface water runoff magnitude and direction may erode slopes and impact stability.
- Effective control of runoff is essential to avoid disruptive consequences.
Membrane drainage systems
- Optimal drainage systems may minimize soil infiltration, therefore preserving slope stability via the regulation of water content and pressure.
- Factors generated by human actions
Construction and development
- The act of excavating and filling a slope may disrupt the inherent equilibrium and result in instability.
- The design and construction techniques must consider these modifications in order to guarantee stability.
Transformations in land use
- Agricultural practices, such as plowing and irrigation, may alter the soil composition and moisture levels, therefore affecting the stability of slopes. Implementing sustainable operations is crucial in order to mitigate adverse impacts.
Metropolis
- Building loads: The inclusion of buildings and infrastructure may augment the load on slopes, hence potentially exacerbating instability if uncontrolled.
- The process of urban expansion often alters the natural drainage patterns, which may result in heightened levels of runoff and erosion.
5.1 Seismic Activity
Seismic-induced shaking
- Ground vibration is the shaking of the ground caused by earthquakes, which may disturb the stability of slopes and possibly result in landslides or soil liquefaction in places that are susceptible to such events.
Key factors to consider in seismic design
- Engineering measures, such as retaining walls and stabilizing measures, are crucial in regions susceptible to seismic activity to limit the hazards linked to slope collapses caused by earthquakes.
What's Your Reaction?