TYPES OF VOLCANOES AND THEIR ASSOCIATED HAZARDS
Explore the different types of volcanoes, their characteristics, and the associated hazards, including lava flows, ashfall, and pyroclastic flows.
The Different Kinds of Volcanoes and the Risks They Pose
- From their role in generating new landmasses to their breathtaking eruptions that have changed entire landscapes, volcanoes have fascinated human imaginations for millennia.
- Actually, there are several kinds of volcanoes, and each has its own special risks and features.
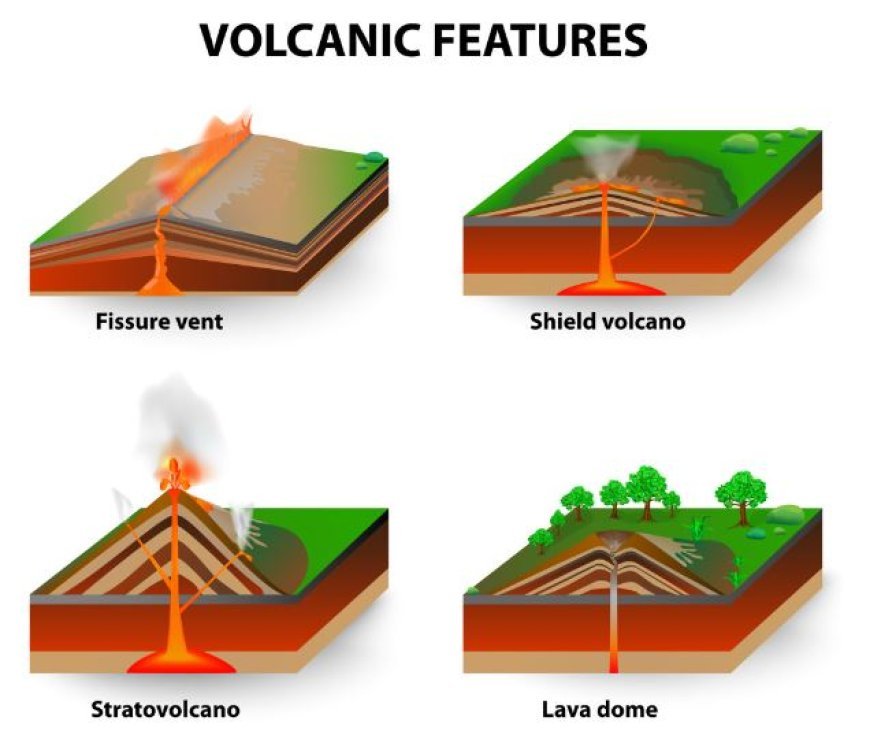
1. Shield volcanoes
- Shield volcanoes are distinguished by their wide, gently sloping conical form, which is reminiscent of the shield used by an old warrior.
- Long-distance movement of fluid basaltic lava from the primary vent, followed by cooling and solidification, is what forms these volcanoes.
- Shield volcanoes include the biggest volcanoes on Earth, such as the Hawaiian Islands.
- Risks: The major way shield volcanoes may cause harm is via slow-moving lava flows, which can submerge large regions, obstruct highways, destroy infrastructure and houses, and result in large financial losses.
- In addition, the chemicals released during eruptions—such as sulfur dioxide—can endanger the health of those living nearby by causing respiratory problems and acid rain.
2. Stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes)
- Stratovolcanoes, also known as composite volcanoes, are conical, steep-sided volcanoes made of volcanic rock, cinders, ash, and solidified lava in different strata.
- Because of their symmetrical, nearly flawless conical shape, iconic stratovolcanoes like Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount St. Helens in the United States are easily recognized.
- Risks: Rock, ash, and gases are frequently violently ejected during stratovolcanoes' explosive eruptions, which are well-known for their destructive nature.
- Volcanic mudflows known as lahars, swift-moving pyroclastic flows, and lava flows are among the dangers connected to these volcanoes.
- Furthermore, ash plumes from stratovolcanoes can impede air traffic and cause breathing problems for people living nearby.
3. Cinder Cone Volcanoes
- The most basic kind of volcanoes are cinder cone volcanoes, which are distinguished by their tiny, solitary cones and steep, conical form.
- Lapilli and volcanic bombs are among the volcanic particles that build up around a central vent to generate cinder cones.
- Hazards: Pyroclastic materials, such as ash and cinders, are ejected during the usually brief eruptions of cinder cone volcanoes, posing a significant risk. Even though the local area around the volcano may be affected by these small-scale eruptions, there is rarely a serious risk to human populations.
4. Lava Domes
- Slow-moving, extremely viscous lava that piles up around a volcanic vent to form a mound or dome-like structure is known as a lava dome.
- The diameter of these constructions can vary greatly, ranging from a few meters to many kilometers.
- Well-known lava domes may be found on Montserrat, the West Indies, where the volcano Soufrière Hills has been producing domes of lava since 1995.
- Dangers: The main way that lava domes may cause danger is by collapsing, which might result in pyroclastic flows that move quickly or block and dam rivers, causing floods or lahars.
- Lava dome development and migration can also cause neighboring regions to lose property and see changes in land use.
5. Caldera Volcanoes
- Caldera volcanoes are created when a volcano collapses into the magma chamber underneath it after a significant eruption, leaving behind a sizable circular depression.
- Many minor volcanic structures, such as smaller cones and hydrothermal vents, may be found inside some of the most well-known calderas on the globe, such as the one in Yellowstone National Park in the United States. These calderas span large regions.
- Risks: The possibility of violent eruptions and the pyroclastic flows that follow, the formation of lahars, and the emission of massive volumes of volcanic gases are the main risks connected to caldera volcanoes.
- Furthermore, because caldera volcanoes are so massive, eruptions may have far-reaching and long-lasting effects, such as altering global weather patterns or drastically changing the ecology.
What's Your Reaction?