LANSLIDES AND CAUSES
Learn about the geological, hydrological, and human-induced factors that trigger landslides.
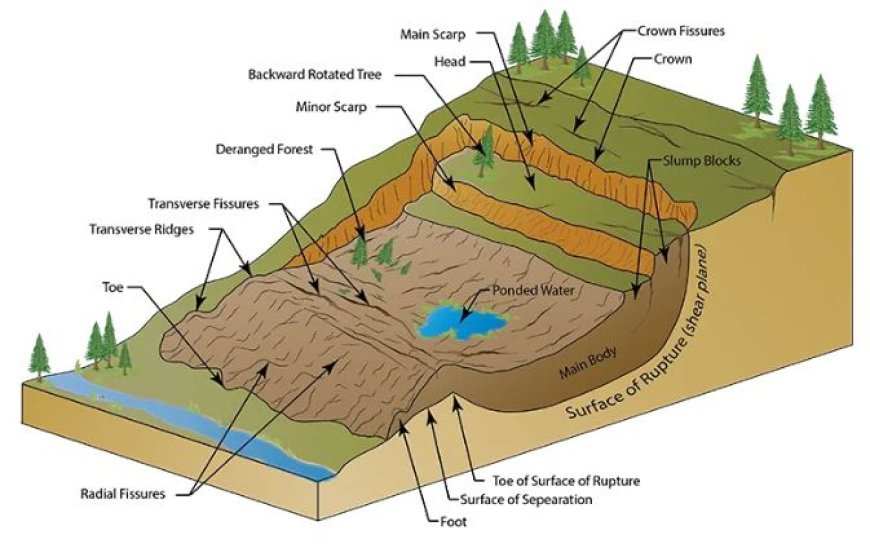
Landslides
- A complex combination of geological, environmental, and human variables drives landslides, also known as mass movements, a widespread phenomenon around the planet.
- These catastrophic occurrences, which include gradual soil erosion and destructive rockfalls, present substantial risks to human life, infrastructure, and the environment.
- Comprehending the origins and consequences of landslides is essential for reducing hazards and establishing sustainable solutions for land management.
Causes of landslides
- Landslides are mostly caused by two main categories: geological propensity and catalytic elements.
- Geotechnically, the intrinsic instability of slopes is frequently a fundamental phenomenon.
- The vulnerability to landslides is further heightened by steep slopes, fragile or broken rock formations, and the existence of unstable soil types such as clay or silt.
- The field of hydrogeology is of utmost importance as water penetration, ground saturation, and the growing amounts of groundwater negatively impact soil cohesiveness and weight, hence increasing its susceptibility to failure.
Triggering Factors
- Geological predisposition establishes the foundation, but extrinsic factors frequently cause slopes to exceed their critical limits.
- Heavy precipitation is a major catalyst, soaking soils and greatly raising pore pressure.
- Seismic activity can tremble loose and unstable slopes, resulting in extensive rockfalls and debris floods.
- Various human activities, including deforestation, mining, building, and inappropriate land use, can worsen these issues by modifying the stability of slopes and disturbing the natural patterns of drainage.
- In addition, climate change is progressively exacerbating the vulnerability to landslides by altering precipitation patterns and intensifying extreme weather phenomena.
Environmental Impacts of Landslides
- The repercussions of landslides spill far beyond their immediate destruction.
- Major repercussions of erosion and sedimentation include the degradation of water quality in rivers and lakes, the damage to aquatic ecosystems, and the jeopardy of infrastructure such as dams and bridges.
- Destruction of habitats is a major consequence, resulting in the decline of biodiversity and disturbing ecological equilibrium.
- Furthermore, landslides can precipitate secondary risks such as tsunamis and dam failures, hence exacerbating the magnitude of devastation.
- Mitigating Landslides: Implementing a thorough approach is essential for mitigating the risks associated with landslides.
- Precipitation monitoring and ground deformation detection-based early warning systems can offer significant advance notice for evacuation and the implementation of protective measures.
- Engineering measures like retaining walls, slope stabilisation schemes, and drainage systems can improve the stability of slopes.
- Land-use planning is essential for restricting growth in areas with a high-risk profile and encouraging sustainable methods such as reforestation and terracing.
- By comprehending the intricate interaction of elements that exacerbate landslides and adopting preemptive actions, we may endeavour to mitigate their catastrophic consequences and safeguard human lives and our environment.
What's Your Reaction?