Energy and Momentum Operators in Quantum Mechanics
In quantum mechanics, operators are mathematical entities that act on wave functions (Ψ) to extract measurable quantities such as energy, momentum, and position. The energy operator (Hamiltonian) determines a system’s total energy and is expressed in terms of kinetic and potential energy components. The momentum operator provides the momentum eigenvalues of a particle and plays a crucial role in linking wave and particle behavior. The kinetic energy operator involves the Laplacian (∇²) and represents the particle’s motion, while the potential energy operator depends on the particle’s position. These operators together form the Schrödinger equation, the foundation of quantum theory. Understanding energy and momentum operators is essential for grasping core principles like wave-particle duality, eigenfunctions, normalization, and quantum formulations such as the Ehrenfest theorem and operator formalism.
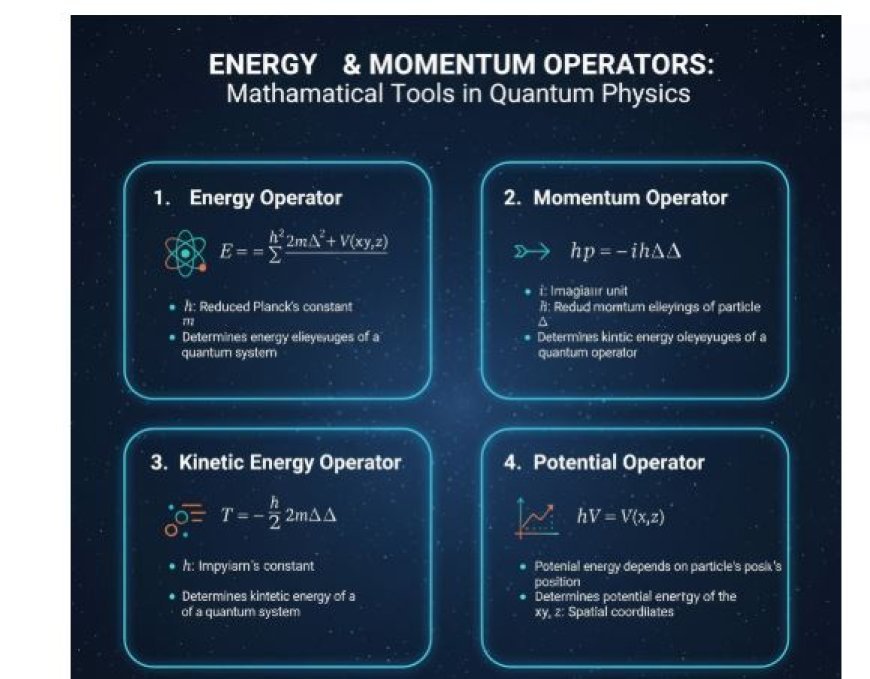
Energy and Momentum Operators
- Operators are mathematical tools that act on wave functions to generate new wave functions.
- In quantum physics, operators describe physical quantities such as energy, momentum, and position.
Energy Operator
- The energy operator is a differential operator used to determine the energy of a particle.
- It is expressed as:
where:
· ℏ is the reduced Planck’s constant (h/2πh / 2\pih/2π),
· m is the mass of the particle,
· ∇2 is the Laplacian operator,
· V(x,y,z) represents the potential energy function.
- The energy operator acts on a wave function to determine the energy eigenvalues of a quantum system.
Momentum Operator
- The momentum operator is a differential operator used to determine the momentum of a particle.
- It is represented as:
where:
· i is the imaginary unit
· ℏ is the reduced Planck’s constant,
· is the gradient operator.
· The momentum operator acts on a wave function to determine the momentum eigen values of a particle in quantum mechanics.
Kinetic and Potential Energy Operators
Kinetic Energy Operator
- The kinetic energy operator is a differential operator used to determine the kinetic energy of a particle.
- It is expressed as:
where:
- ℏrepresents the reduced Planck’s constant,
- m is the mass of the particle,
- ∇2 is the Laplacian operator.
- The kinetic energy operator acts on a wave function to determine the kinetic energy of a quantum system.
Potential Energy Operator
- The potential energy operator depends on the position of the particle.
- It is generally represented as:
where x,y,zx, are the spatial coordinates of the particle.
- The potential energy operator acts on a wave function to determine the potential energy of the system.
What's Your Reaction?