LIGHT EMITTING DIODE
Light-emitting diode (LED): Tiny chip, big impact - converts electricity directly into light.
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
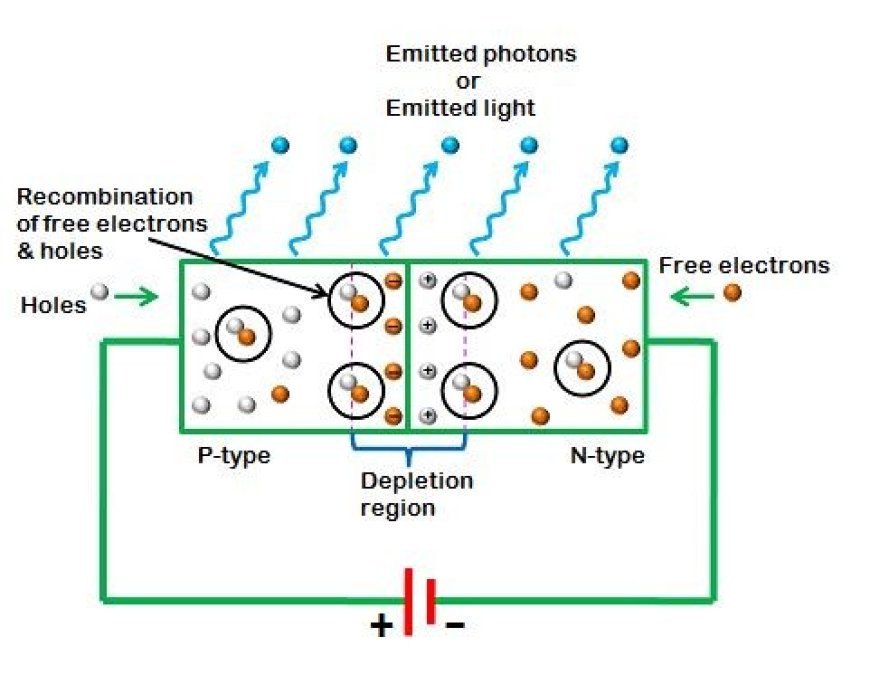
- An LED is a p-n junction diode that has been highly doped and is used in forward bias.
- We already know that the n side has a lot of electrons and the p side has a lot of holes.
- When electricity is put into a diode with forward bias, electrons move from the n side to the p side, which has holes.
- The release of a photon, which is the light we see in LEDs, happens when one electron and one hole come together.
Working of an LED
Properties of an LED
- The amount of light an LED gives off is directly related to the amount of current it has. This is because more current means more photons are released, which means more light.
- It depends on the semiconductor's band gap (the space between the conduction band and valence band) and what color the light it gives off is.
- An LED's reverse breakdown voltage is low.
- Only compound semiconductors, such as GaAs, can be used to make LEDs.
Symbol for LED
In physics, the following symbol can be used to show an LED:
LED Symbol Advantages of LED
It saves energy
- LEDs turn almost all the electricity they use into light energy, and only a small amount is lost as heat.
Superior light quality
- LED lights only shine in one way, unlike other types of lights.
- It means that LEDs only give off light in one way. This makes it a better power source than the others.
Highly durable and easy to maintain
- LEDs don't have any glass or fiber parts like other light sources do, so they last a long time. This type of lightning is called "solid-state lightning," or SSL.
- Most modern LED makers use high-quality metals and aluminum for their parts, which makes them even more durable.
Require little to no warm-up time
- Unlike traditional bulbs, LEDs light up right away and don't need much to no warm-up time.
- Any LED gadget will light up in a few microseconds, and ones that are used for transmission can actually respond even faster.
Easily portable
- LEDs are small, so they are easy to carry and can be connected to printed circuit boards.
- You'll save a lot of money on your power bill because LED lights use 5–6 times less energy than regular lights to produce the same amount of light.
It offers varying color intensity
- LED lights have a wider range of CCT than other sources.
- "CCT" stands for "Correlated Color Temperatures."
- " A higher number means that the light is bright and cool. The smaller number, on the other hand, means warm lights.
- While incandescent lighting's CCT spectrum ranges from 2,000K to 6,000K, LEDs' range is from 1,000K to 10,000K, making it a more flexible choice for many uses.
- Smart lights that change colors are one type of technology that is becoming more popular in homes.
- LED lighting that is set up correctly is also helpful in hospitals and senior homes.
- LED lights last a long time. Unlike incandescent and fluorescent lights, LED lights don't have wires, so they last longer.
- A CFL can last up to 12 years, which is 40 times longer than that of a regular light bulb.
Low maintenance
- The cost of maintaining LED lights is much cheaper than that of maintaining traditional lighting tools because they last a long time.
It's easy to dim
- A pulse-width modulator lets you lower the forward current going to an LED bulb to make it less bright.
- You can see this same reason why car headlights look like they flash when you look at them with your own eyes or a camera.
More reliable
- As LEDs age, they dim instead of turning off all of a sudden.
- LED lights are better for the earth because they don't contain any potentially harmful chemicals like mercury like other light sources do. On top of that, it can be recycled and doesn't make a lot of e-waste.
Disadvantages of LED
Very easy to harm if not planned correctly
- An LED will only last longer if it is well-designed and has a good heat sink.
- If the heat sink is too small or doesn't exist at all, the heat that is produced during operation won't be able to escape. This will shorten its life.
- LED lights are a pricey choice because they cost a lot more than regular light bulbs.
Require special controllers
- A lot of LED lights need to be fixed with regular light dimmers.
- So, putting a little money into dimmers that work with LEDs is a must and will pay off in the long run.
An unreliable light quality
- LEDs, especially cool-white LEDs, are not the same as any black body heater, like an incandescent light.
- Its sharp peak at 460 nm and dip at 500 nm make it hard to see the colors of things that are close by.
No individual replacement
- Most LEDs are built in a way that doesn't let you change just one LED. You have to replace the whole lighting device. It might cost a lot and be difficult.
- High voltage can damage an LED because it is sensitive to both voltage and current.
- A low cutoff voltage and a high current that is too high for the device can damage it.
Harms of blue light
- Some studies show that blue and cool-white LEDs give off more blue light than other types of light.
- LEDs can only provide a circular field of light because they aren't very close to a point source and instead have a Lambertian distribution.
What's Your Reaction?