FIRST ORDER AND SECOND ORDER LOW PASS FILTER
Low pass filters let low frequencies through: first order with a gentler (-20 dB/decade) roll-off, second order with a steeper (-40 dB/decade) cut.
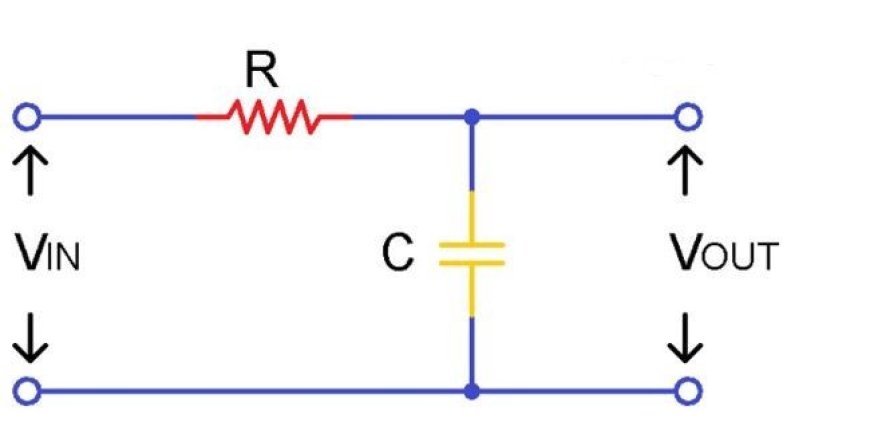
Low-Pass Filter
- The low-pass filter, or LPF, is a type of filter that lets low-frequency signals through but mutes high-frequency sounds above a certain cut-off frequency.
- The design of the low-pass filter has the most impact on its frequency response.
- These filters come in different shapes and sizes, and they make signals clearer.
- Designers often use these filters as prototypes because they have a single frequency and low resistance.
- The sample is used to find the best resistance and bandwidth, which then turns into the best band type, such as low-pass (LPF), high-pass (HPF), band-pass (BPSF), or band-stop (BSF).
Low Pass Filter Using Op Amp
- Operating amplifiers, or Op-Amps, make low-pass filters that work very well without the need for inductors.
- The basic parts of a filter can be combined with an op-amp's feedback loop, making it easy to make high-performance LPFs with only the necessary parts (except for the inductors).
- The op-amp LPF is used in many places, from power sources to the outputs of DACs (Digital to Analog Converters) to get rid of alias signals and for other reasons.
Make a low-pass filter with an op-amp
- Operating amplifiers, or Op-Amps, make low-pass filters that work very well without the need for inductors.
- The basic parts of a filter can be combined with an op-amp's feedback loop, making it easy to make high-performance LPFs with only the necessary parts (except for the inductors).
- The op-amp LPF is used in many places, from power sources to the outputs of DACs (Digital to Analog Converters) to get rid of alias signals and for other reasons.
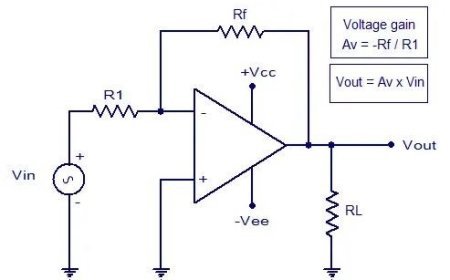
First-Order Active LPF Circuit Using Op-Amp
- Here is a picture of the single-pole or first-order active low-pass filter's circuit.
- A capacitor is placed across the feedback resistor in the op-amp low-pass filter circuit.
- When the frequency goes up in this circuit to raise the feedback level, the reactive resistance of the capacitor goes down.
Input Op Amp for a Low Pass Filter of the First Order
- The frequency at which the reactance of the capacitor can match the resistance of the resistor can be used to figure out this filter.
The following method can be used to get this:
Xc = 1/π f C
Where "Xc" is the capacitive reactance in ohms, "π" is a standard letter, 3.412 is its value, and "f" is the frequency in hertz (Hz). In units of farads, "C" stands for capacitance.
- Taking away the capacitor's effect makes it easy to figure out the in-band gain of these circuits.
- You can use these kinds of circuits to lower the gain at high frequencies and reach a maximum speed for roll-off of 6 dB for each octave.
- This means that the o/p voltage drops for each frequency repeat. This type of filter is called a first-order or single-pole low-pass filter.
Using an op-amp for a second-order active LPF circuit
It is possible to make filters with a wide range of different gain levels and roll-off models by using an operating amplifier. This filter has both a frequency reaction and a gain of 1.
Using an op-amp for a second-order active LPF circuit
- For the reaction of the Butterworth low-pass filter and unity gain, it's easy to figure out the circuit numbers.
- These circuits need a lot of damping, and the ratio numbers of the capacitor and resistor show this.
f = 1 – √4 π R C2 R1 = R2 C1 = C2
- It is important to make sure that the resistor's values drop between 10 kilo-ohms and 100 kilo-ohms when you choose the values.
- This is important because the frequency makes the circuit's o/p impedance go up, and changing the numbers in this part may change how it works.
Low-Pass Filter Applications
The following are some uses for a low-pass filter:
- In telephone systems, low-pass filters change the sound waves in the speaker to a voice-band signal that is limited in time.
- LPFs are used to get rid of high-frequency signals, or "noise," from a circuit. When the signal goes through this filter, most of the high-frequency signals are removed, and a white noise can be made.
- In picture processing, a low-pass filter is used to make an image better.
- Because they are used in sound, these filters are sometimes called treble cuts or high cuts.
- A low-pass filter is used in an RC circuit. This type of filter is called an RC low-pass filter.
- Like an RC circuit, LPF is used as an integrator.
- In multi-rate DSP, LPF is used as an anti-imaging filter while an interpolator is running.
- In the same way, this filter is used as an anti-aliasing filter when a decimator is run.
- For baseband signals to work well in devices like the super heterodyne, low-pass filters are used.
- A low-pass filter is used to make signals from medical devices that come from the body less frequent while sensors are being used for tests. So these signals can go through the LPF to get rid of some background noise that you don't want to hear.
- These filters are used to change the duty cycle amplitude and find the phase in the phase-locked loop.
- In AM radio, the LPF is used for the diode detector to turn the AM-modulated intermediate frequency signal into an audio signal.
What's Your Reaction?