EFFECT OF ISOTROPIC SUBSTITUTION
Isotropic substitution involves replacing a system component with a material having identical properties in all directions, affecting mass, volume, elasticity, and conductivity. Used in composites, structural reinforcement, and biomedical engineering, it enhances strength, stability, and performance while maintaining uniform physical behavior.
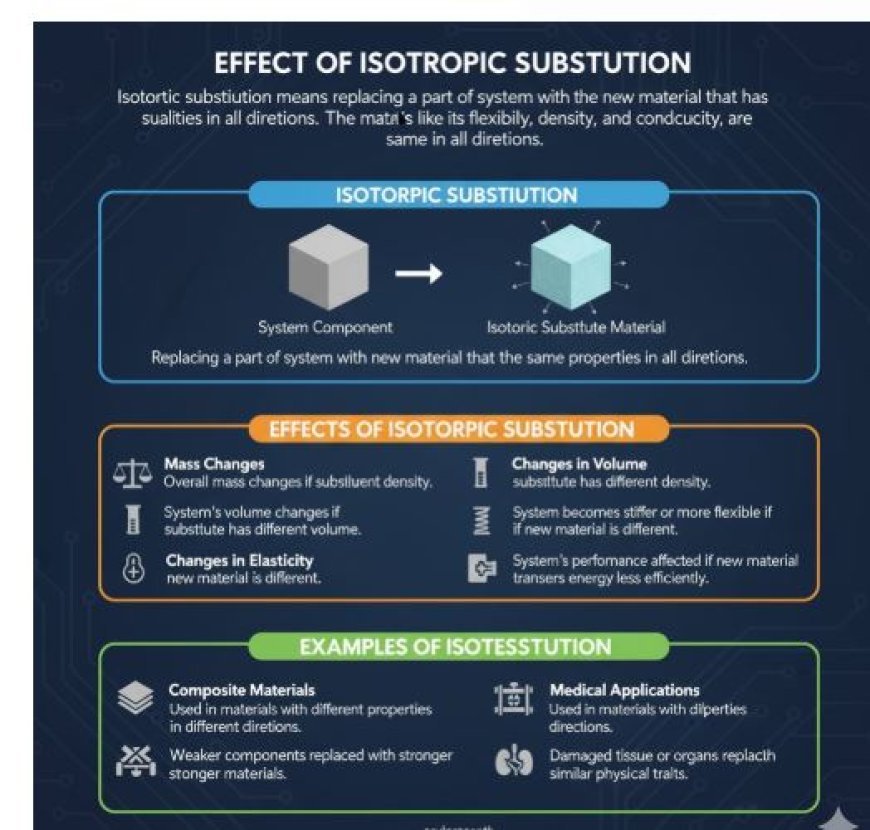
Effect of Isotropic Substitution
Isotropic Substitution
- In physics, isotropic substitution means replacing a part of a system with a new material that has the same qualities in all directions.
- The material's traits, like its flexibility, density, and conductivity, are the same in all directions.
Isotropic Substitution and Its Effects
- Isotropic substitution can have a significant impact on how a system functions. Here are some of its effects:
- Mass changes: If you replace a part of a system with a material that has a different density, the system's overall mass will change.
- Changes in volume: The system's volume will change if the substitute material has a different volume than the original material.
- Changes in elasticity: If the new material is more or less flexible than the old material, the system may become stiffer or more flexible overall.
- Differences in conductivity: If the new material does not transfer energy or heat as efficiently as the old material, the system’s performance may be affected.
Examples of Isotropic Substitution
- Composite materials: Isotropic substitution is used in composite materials that have different properties in different directions.
- Strength enhancement: Weaker components can be replaced with stronger materials to make structures more resistant to damage or stress.
- Medical applications: Isotropic substitution is used in biomedical engineering, where damaged tissue or organs are replaced with materials that have similar physical traits.
What's Your Reaction?



































