VIBRATING DIATOMIC MOLECULES AND DIATOMIC VIBRATING ROTATORS
Learn how diatomic molecules vibrate and rotate simultaneously, forming quantized energy states that influence spectra, bonding, and thermodynamic behavior—key to understanding gas properties, chemical reactions, and molecular motion in physics and chemistry.
Vibrating Diatomic Molecules and Diatomic Vibrating Rotators
Introduction to Diatomic Molecules
- A diatomic molecule consists of two atoms. These atoms can be either:
- Identical elements, such as oxygen (O₂).
- Different elements, such as carbon monoxide (CO).
- Common examples of diatomic molecules include oxygen (O₂), nitrogen (N₂), and hydrogen (H₂).
How Molecular Vibration Works
Vibration
- Molecular vibration refers to the back-and-forth motion of atoms around their equilibrium positions.
- This movement is influenced by interatomic forces, which can be explained using potential energy concepts in physics.
Types of Vibrations
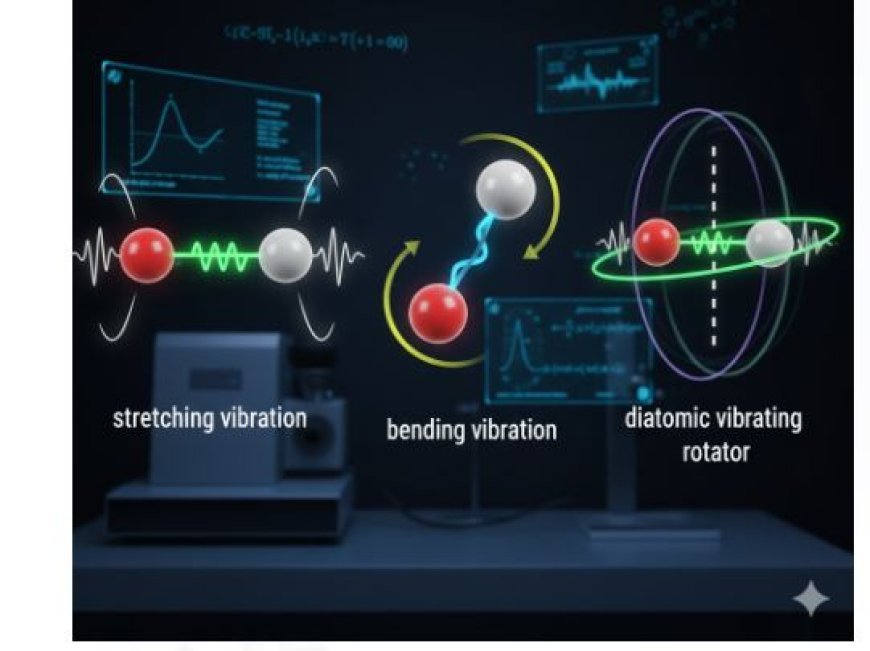
- Stretching Vibration
- Occurs when the bond between two atoms expands and contracts.
- Similar to pulling and releasing a spring—it stretches and then returns to its original position.
- Bending Vibration
- Involves a change in the bond angle between atoms.
- Similar to bending a flexible stick, where atoms shift their relative positions.
Diatomic Vibrating Rotators
Concept of Vibrating Rotators
- Diatomic molecules exhibit both vibrational and rotational motion.
- The molecule can vibrate while also rotating around its center of mass, making its motion more complex.
Properties of a Vibrating Rotator
- Rotation
- The molecule can spin around an axis that passes through its center.
- This rotation plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of molecules in different states (gas, liquid, etc.).
- Energy Levels
- Molecular energy is quantized, meaning it exists in discrete levels.
- Both vibration and rotation contribute to the molecule’s energy.
- When vibration and rotation occur simultaneously, the molecule enters a higher-energy state compared to its resting state.
Mathematical Representations
- The behavior of vibrating rotators can be described using quantum mechanics.
- Key mathematical equations explain how:
- Energy levels change.
- Molecules transition between different energy states.
Importance of Diatomic Vibrating Rotators
In Chemistry
- Essential for understanding molecular interactions.
- Helps explain chemical reactions, bonding, and thermodynamics.
In Physics
- The diatomic vibrating rotator model explains:
- Spectral lines of gases.
- Specific heat capacities of substances.
- Connects molecular properties to observable macroscopic phenomena.
What's Your Reaction?