SPECIFIC CAPACITY OF SOLID
The specific heat capacity of a solid is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of that solid by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin).
- Matter can be roughly broken down into three states: solid, liquid, and gas. By giving them the right temperature and pressure, you can change their bodily states. The same method can also be used to change their balance points.
- For any kind of matter to raise or lower its temperature, it needs energy from somewhere else. There isn't much change in temperature when gases are heated, but there are big changes in other things. Pressure and volume are these things.
- You can think of a substance's specific heat capacity as the amount of energy it takes to raise its temperature by one degree Celsius per unit mass.
Specific heat capacity of solids
- Solids are types of matter that have strong forces between their molecules, are hard, have the right shape and structure, and so on.
- Since things can be heated, it is possible to find out how much specific heat they can hold. This amount of heat is measured in SI units, which are J/kg/K.
- One unit mass of any solid material needs a certain amount of energy to raise its temperature by one degree Celsius. It has a certain amount of heat capability.
- We will need to use the law of equal distribution of energy to find the specific heat capacity.
- If the temperature of a system is equal, this rule says that there will be a certain amount of average energy for each degree of freedom a molecule has.
- For instance, a gas molecule moving in three-dimensional space has three coordinates, which means that molecule has three degrees of freedom.
- Let's look at any solid that has N atoms. There is only one plane of coordinates, or 1D space, in which each atom can move freely. Here's how to figure out the total energy.
U: U = 3kbTNA = 3RT
The following equation will be used to show the first rule of thermodynamics:
ΔQ = ΔU+P ΔV
- The first rule says that energy can only change forms; it can't be added to or taken away.
- In this case, PV doesn't need to be used because the volume change for solids is so small.
- So, to find the molar specific heat capacity (the amount of heat that can be stored in one mole
- The outcome is C =Q / T = U / T
C = 3R = 24.94 J/K-1 mol-1 C
- It's called ∆T and Q is the amount of heat that is given.
- The ability to hold heat is pretty much a trait that comes with it. This means that it is a property of a certain material.
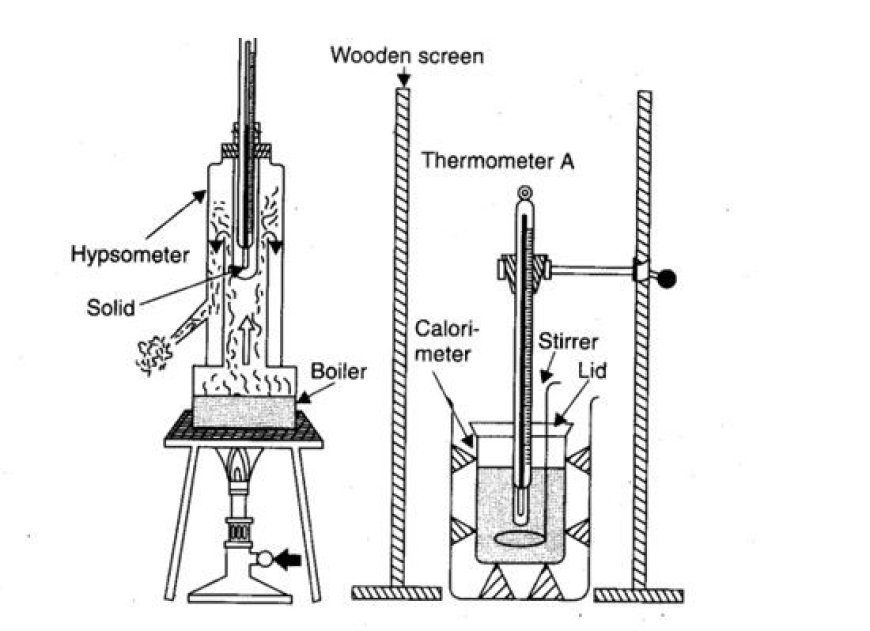
- A calorimeter is used to figure out the heat capacity.
- The bomb calorimeter always shows the same volume readings.
- The coffee cup calorimeter is a different type of calorimeter used to find the heat capacity at steady pressure.
What's Your Reaction?