SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Discover the principles and applications of satellite remote sensing, including its role in understanding Earth's surface and monitoring environmental changes.
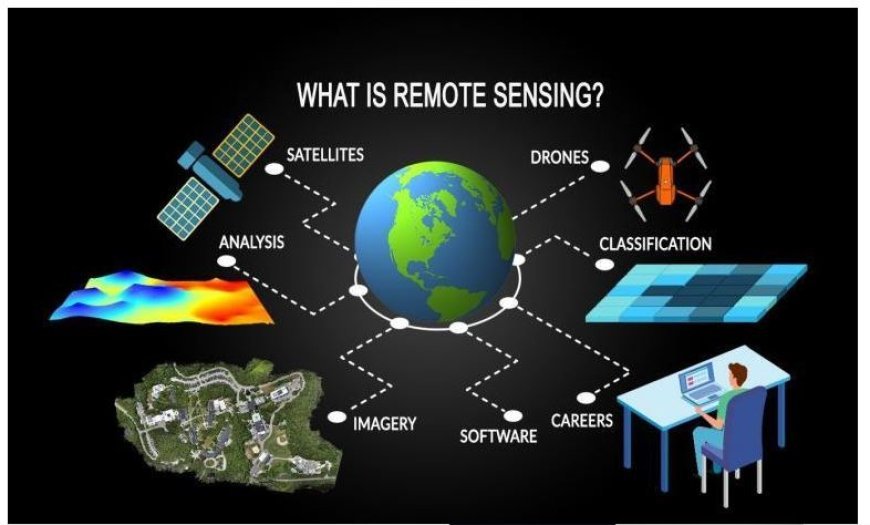
Satellite Remote Sensing
Introduction
- Satellite remote sensing is an advanced technique that utilizes orbiting satellites to collect data about the Earth.
- While traversing a region, these satellites capture images and gather data without making physical contact.
Operational Mechanism
- Operational Mechanism refers to the system or process by which an organization or machine functions and carries out its tasks.
- Satellites operate at altitudes ranging from 600 to 36,000 kilometers above the Earth as they traverse through space.
- These satellites possess several sensors and cameras, enabling them to gather data over a broad spectrum of light bands.
- Data Collection: The satellites' sensors quantify the electromagnetic energy emitted or reflected by the Earth's surface.
- Data transmission: After the collection of this information, it is transmitted back to Earth, where experts scrutinize it in order to get further insights into the surrounding environment.
Various Categories of Satellite Sensors
- Optical sensors function similarly to conventional cameras since they capture images using visible light.
- Monitoring land usage, vegetation, and urban expansion is particularly convenient with them.
- Radar sensors employ radio waves to see the Earth's surface, regardless of cloud cover or nighttime conditions.
- Consequently, they are valuable for assessing the conditions of both land and water.
- Thermal devices are designed to detect and capture the thermal energy emitted by the Earth. Thermal cameras are crucial tools for analyzing temperature variations, detecting fires, and monitoring fluctuations in water temperature.
Utilizations of Satellite Remote Sensing
- Environmental monitoring: Deforestation: Satellites are highly valuable for monitoring and detecting unauthorized logging activities, as well as tracking changes in forested areas.
- Climate Change: It provides valuable data on fluctuations in temperature, melting of glaciers, and sea level.
- Agriculture: Crop Monitoring: Satellite imagery enables farmers to monitor the condition of their crops, forecast their harvests, and optimize water management strategies.
- Soil analysis involves the use of satellites to assess the soil conditions, aiding farmers in making informed decisions on crop selection and other agricultural activities.
- Urban Planning: City Expansion: Urban planners may utilize satellite imagery to monitor and analyze the dynamic process of urban growth and transformation.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Infrastructure Monitoring is the vigilant observation of modifications to components such as roads and buildings that constitute the infrastructure.
- Anthropogenic disasters: Satellites rapidly survey regions affected by natural calamities such as cyclones, inundations, and seismic events, hence facilitating disaster response.
- Wildfire surveillance involves the detection and continuous monitoring of wildfires, enabling the prediction of their progress and facilitating the prompt evacuation of persons and allocation of resources.
The Importance Of Satellite Remote Sensing
- Data Accessibility: Satellites provide scientists, government agencies, and the public with valuable information, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize resource management.
- Global Perspective: This technology provides us with a comprehensive view of the Earth, enabling us to comprehend phenomena occurring on a worldwide level, such as climate change and shifts in population.
- Cost savings: Satellites offer a more cost-effective and extensive means of observing and monitoring compared to ground-based data collection methods.
- Researchers in the fields of meteorology, oceanography, and geography rely on satellite data for their study and technological advancements.
- Furthermore, it enhances the advancement of technology and the refinement of data analysis procedures.
What's Your Reaction?