ENERGY INTERACTION IN THE ATMOSPHERE AND WITH THE EARTH
Explore the complex interactions between the atmosphere, Earth's surface, and energy, and their significance in remote sensing and understanding Earth's systems.
Energy: The Driving Force
- Energy is the ability to make things happen or do work. It comes in many forms, such as light, heat, and motion, all of which are necessary for life as we know it.
- Energy is the planet's lifeblood; it controls weather trends, shapes the climate, and keeps life going.
- It gives life to the Earth's complex systems that keep it moving and changing.
The energy in the air
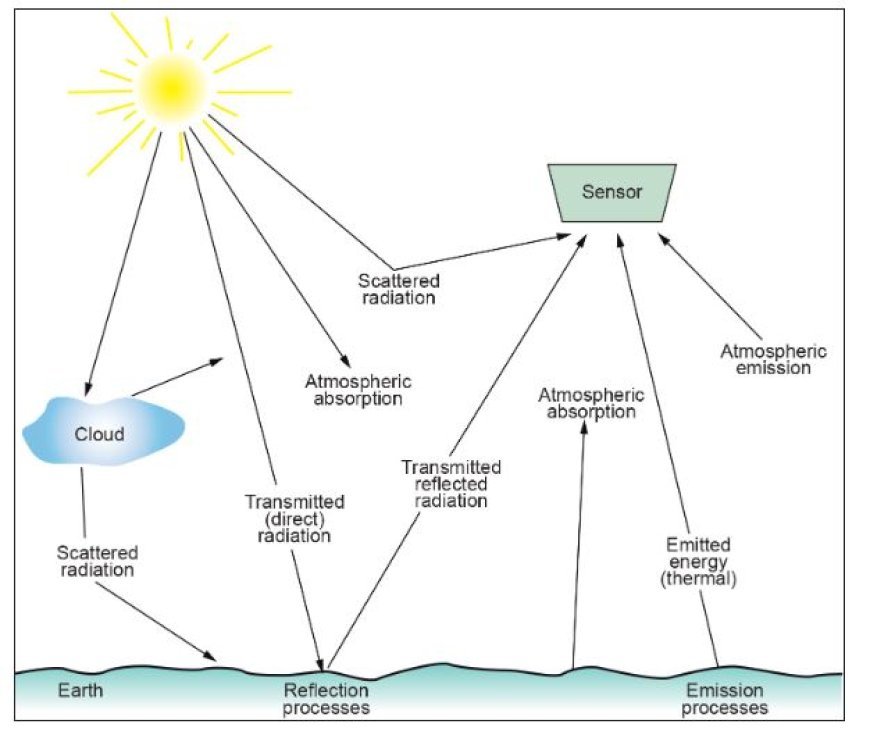
Think of the atmosphere as a huge pool of gases that is always moving and being changed by the energy it takes in. This is how energy moves around in this moving layer:
1. Solar energy
- The Sun's Gift: The Sun, which is our star, lights up the whole universe with energy.
- The main source of all energy exchanges on Earth is this light energy.
- The atmosphere, seas, and land all soak up some of the sunshine that hits Earth, which warms them up.
- Though clouds, ice, and even the Earth's surface can bounce some of it back into space.
2. Methods of Heating and Cooling
- As a result of being less thick, warm air rises, and cooler air falls, making constant convection currents.
- This changing process moves energy around in the atmosphere, which affects how the wind blows and how the weather changes.
- Radiation: How the Earth Responds: The Earth sends energy back into the air as infrared radiation, which is a form of heat, after taking it in from the sun.
- To keep the Earth's temperature stable, this process helps keep the balance of heat.
3. Weather Patterns:
- Uneven Distribution: The Earth's surface receives different amounts of energy from the sun.
- This uneven spread causes different weather trends.
- For example, tropical areas tend to be warmer than cold areas.
- Storm Formation: Energy from warm air is very important for storm growth.
- The rise of warm, wet air makes the conditions unsteady enough for hurricanes, thunderstorms, and other weather events to happen.
4. The Greenhouse Effect
- Heat Trapping: Gases in the air, like carbon dioxide and methane, are known as greenhouse gases and they keep heat inside.
- This natural process keeps Earth warm enough for life to survive, making it a place where people can live.
- Concerns about the environment: However, too much of these gases can cause too much heat, which changes weather trends and contributes to climate change.
Energy at the Earth's Surface
- The landforms and pools of water that make up the Earth's surface are also very important to the energy flow.
Let us look at how energy affects these different things:
1. Absorption and Reflection
- Surface Differences: Different materials receive and reflect sunlight in different ways. Dark things, like woods, take in more heat than light things, like ice or sand.
- Different levels of absorption have an impact on the temperature and vegetation in the area.
- How hot or cold the surface is depends on how much energy it absorbs. This affects how the area climate changes.
2. Heat Transfer: A Flow of Energy
- From the Sun to Earth: Energy from the Sun hits Earth through conduction, which sends heat straight to the top of the Earth.
- The air above the warm surface then gets warmer.
- Solar energy warms pools of water, which makes some of it escape and rise into the air.
- This cools and moistens the environment.
- The surface cools down and the air gets more wet, which causes clouds to form and rain to fall.
3. Water Bodies: Thermal Reservoirs
- Heat storage: Oceans and lakes soak up and store a lot of sun energy like huge thermal reserves.
- The energy stored in these bodies of water changes the way the weather works, which is why coastal climates are warmer than climates in the interior.
4. Plants and landforms: Changing the Flow of Energy
- Energy Conversion and Climate Control: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants take in energy from the sun and turn it into food.
- They also change the weather in the area by transpiration, which is the release of water vapor into the air.
- Landforms: How Energy Is Spread Out: Mountains can block winds and cast rain clouds, which changes how energy is spread out in different areas.
What's Your Reaction?