ENTROPHY
Entropy: The Universe's one-way street towards disorder, as measured by energy dispersal.
Entropy
- Although you are right that entropy is "less" in a solid, it's important to keep in mind that entropy is usually given as a number.
- It is shown by the sign S, and figuring it out depends on a lot of different things, such as the basic Boltzmann constant (k) and the number of microstates (possible microscopic arrangements) that the system can have.
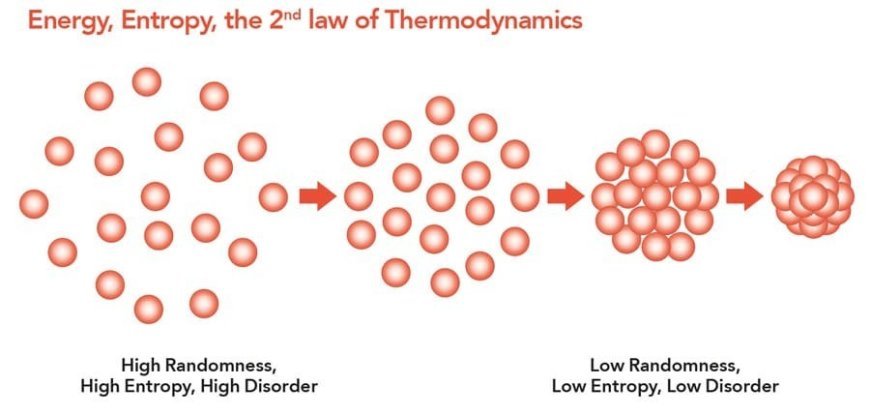
Entropy and Disorder
- It makes a lot of sense that entropy and chaos are related. When entropy is high, there are more ways that the system's parts could be arranged, which makes the state more "spread out" and disordered.
- On the other hand, smaller entropy means that things are more organised and orderly, and there are fewer possible outcomes.
Applications of Entropy
It is very important to understand entropy in many areas, such as:
Chemistry: Figuring out what will happen with random reactions and phase changes (like ice melting) by looking at how entropy (ΔS) changes. In exothermic reactions, ΔS usually goes down, which means that things are moving in a more ordered way. On the other hand, in endothermic reactions, ΔS usually goes up because energy is being spread out.
Physics: Using the idea of rising entropy in a closed system to explain things like the direction of heat flow and how well motors work.
Cosmology: Looking into the idea of the universe's "heat death," which would happen when chaos reaches its highest point and there is no more energy flow or chance for change.
What's Your Reaction?