ENTROPHY AND LAW OF THEROMODYNAMICS
Entropy: Universe's law of increasing disorder, where usable energy scatters over time.
Thermodynamics
- The words "thermo" and "dynamics" make up the word "thermodynamics." "Thermo" means heat, and "dynamics" means force that moves something mechanically.
- So thermodynamics is the branch of physics that looks at how heat and other types of energy fit together.
- Setting up a clear limit makes physics a lot easier to understand. The "surroundings" are everything that is not inside the limit, and the "system" is everything that is inside it.
- After making the boundary map, the flow across system borders can be used to show how energy moves and is transferred. There is a world outside of the system called the "universe."
Thermodynamics
In physics, thermodynamics is the study of energy, heat, and temperature, as well as how they relate to radiation, energy, and the way things are physically.
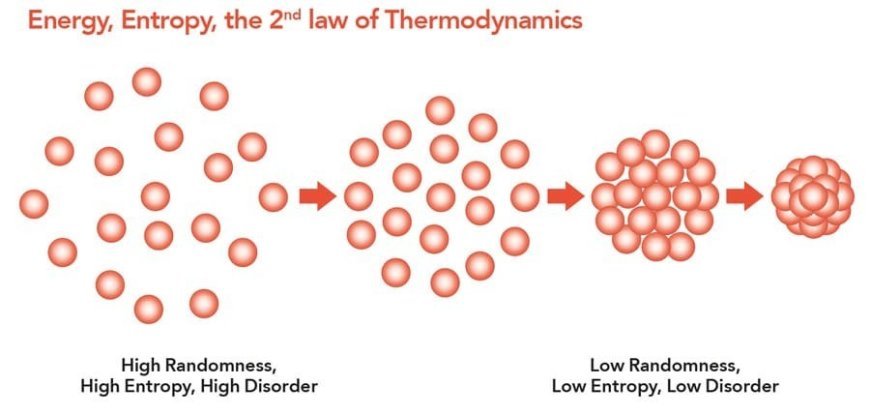
Entropy
- It is the amount of heat energy per unit of temperature in a system that can't be used to do work.
- Since work is made when molecules move in a planned way, entropy is a way to measure how molecularly chaotic or random a system is.
- Entropy theory helps us fully comprehend the direction of change that happens on its own in a wide range of everyday situations.
The Laws of Thermodynamics
- When a thermodynamic system is in thermal balance, it has basic physical constants like energy, temperature, and entropy.
- Thermodynamic laws determine these. These thermodynamic rules explain what these amounts do in various scenarios.
- There are four rules that govern thermodynamics. Here they are:
1. The first law of thermodynamics.
2. The second law of thermodynamics.
3. The third law of thermodynamics.
4. The zeroth law of thermodynamics.
- The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics says that if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, then the first two bodies are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
- In other words, if system A is thermally balanced with system B and system C is also thermally balanced with system B, then both systems A and C are thermally balanced.
The First Law of Thermodynamics
- The first rule of thermodynamics says that energy can't be made or broken down, but it can be changed from one form to another. This is the first thermodynamic rule.
- It talks about heat, internal energy, and work. The first rule of thermodynamics says that energy can't be made or broken down, but it can be changed from one form to another.
- This law says that some of the heat that is sent to a system is used to change the energy inside it, and the rest is used to do work.
- The first law of thermodynamics is also known as the law of conservation of energy.
This is how the first law of thermodynamics is represented in mathematics:
In math terms, it can be written as Q = U + W.
When heat is given or lost, the symbol ΔQ is used.
U stands for the change in energy inside the body.
W means "work done."
Another way to write the above equation is as follows:
ΔU = ΔQ – W
- Based on the above equation, we can say that the route taken to change the state has no effect on the amount (¦Q + W).
- Also, when heat is added to a system, its internal energy begins to grow, and the same is true when cold is added.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
- The second law of thermodynamics says that entropy always rises in a system that is kept separate from other systems.
- Any system that is kept separate moves on its own towards thermal equilibrium or the state with the most chaos. The chaos of the world never goes down; it always goes up.
The Third Law of Thermodynamics
- As the temperature gets closer to zero, the third rule of thermodynamics says that the entropy of a system gets closer to a constant number.
- When the temperature is 0 degrees Celsius, there is no entropy in a pure crystalline material. This statement is true if the perfect crystal only has one state with the least amount of energy.
What's Your Reaction?