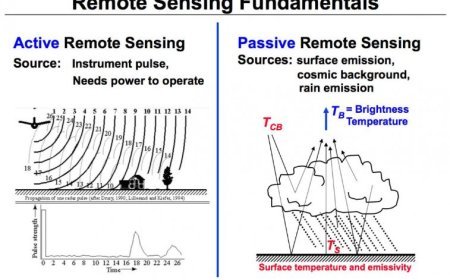
ELEMENTS OF PHOTO AND IMAGE INTERPRETATION IN REMOTE SENSING
Learn about the elements of photo and image interpretation in remote sensing, including visual cues and digital techniques.
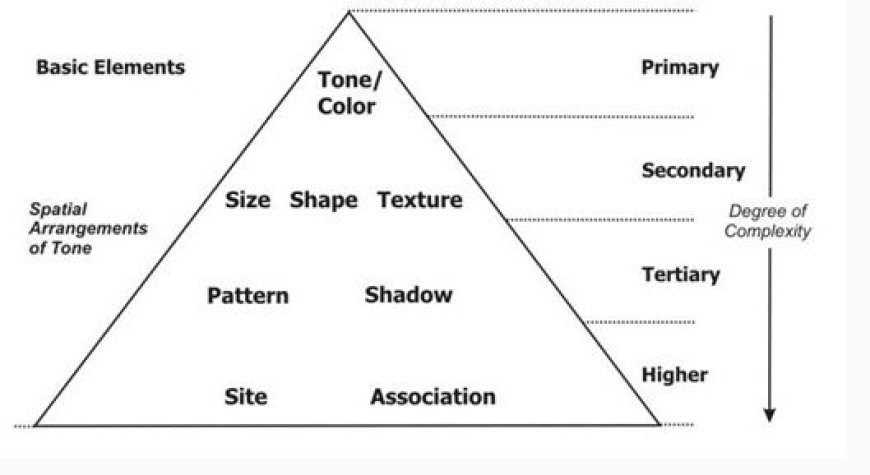
Elements of Photo and Image Interpretation in Remote Sensing
Types of Resolutions
- Remote sensing imagery is classified into several sorts of resolutions, each of which is important for proper picture analysis:
- Spatial Resolution: This metric measures the smallest item observable in a picture. High spatial resolution allows for more detailed and accurate imaging.
- Spectral Resolution: Spectral Resolution refers to a sensor's ability to discern small wavelength intervals.
- Greater spectral resolution, acquired by the addition of spectral bands, improves the discrimination between materials.
- Temporal Resolution: This describes how frequently a satellite returns to the same area, which is critical for tracking and assessing temporal changes in the environment.
Fundamentals of Image Interpretation
2.1 Contextual Understanding
- An in-depth grasp of the context is required for accurate image interpretation.
- This encompasses geographical, historical, and environmental circumstances that may influence interpretation.
- Recognizing seasonal variations in vegetation, for example, can have an impact on plant health assessments.
2.2 Image Composition
- Image composition is examining how different parts are organized inside an image. Key features include:
- Tone: A change in brightness or darkness that aids in determining the material properties of objects.
- Texture: Texture is the surface quality of things, such as smoothness or roughness, that helps distinguish land use and plant varieties.
- Shape and Size: Knowing the shapes and sizes of things helps you distinguish between natural formations and man-made buildings.
2.3 Color Analysis
- Color in remote sensing photos corresponds to the spectral bands collected by the sensor. Different materials have unique color properties.
- Using color indices, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), can help interpret factors like vegetation health.
2.4 Feature Extraction
- Feature extraction is the process of extracting certain properties within photographs, such as buildings, roads, or bodies of water. This technique involves:
- Supervised Classification: In order to train the classification algorithm, this technique requires prior information and labeled examples.
- Unsupervised Classification: This approach groups data based on inherent qualities, eliminating the requirement for pre-labeled training data.
Tools and Techniques for Image Analysis
3.1 Software Tools
- Several software tools help understand remote sensing images:
- Geographic information systems (GIS) provide tools for managing, analyzing, and displaying geographical data.
Picture Processing Software
Applications like ENVI and ERDAS IMAGINE offer extensive features for thorough picture analysis.
3.2 AI and ML
- The combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) improves remote sensing picture interpretation by automating feature extraction and pattern identification, resulting in more accurate data processing.
Challenges of Image Interpretation
4.1 Environmental Effects
- Various environmental conditions, such as clouds, haze, and atmospheric distortion, can have a detrimental influence on image quality.
- Using corrective procedures is critical for improving image clarity and accuracy.
4.2 Data Management
- The vast amount of data generated by remote sensing satellites might be intimidating.
- Effective data management techniques and prioritizing are critical for ensuring relevant interpretation while avoiding analysis overload.
What's Your Reaction?