FUNDAMENTALS OF REMOTE SENSING
Understand the fundamentals of remote sensing, including the electromagnetic spectrum, radiation, and energy interactions.
Fundamentals of Remote Sensing
- We can obtain information about the Earth's surface from a distance thanks to the exciting field of remote sensing.
- It is extensively utilized in agricultural, urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.
Remote Sensing
- Definition: Remote sensing is the process of gathering information about a subject or location from a distance, typically using satellites or airplanes.
- How It Operates: These platforms sensors use a variety of energy waves, such as radar, infrared, and visible light, to gather data.
Types of Remote Sensing
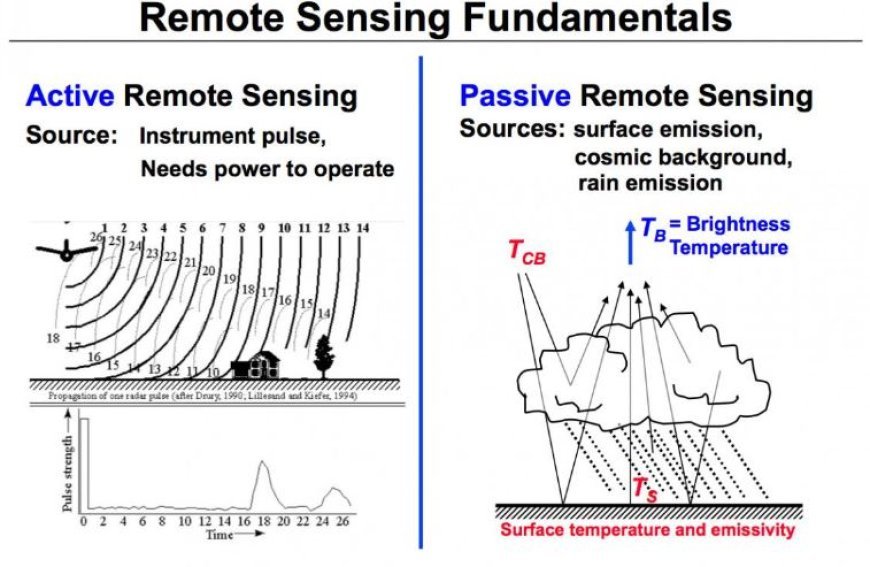
- Passive Remote Sensing
Synopsis: This kind of remote sensing depends on renewable energy sources, such as sunshine.
Examples: Cameras that take pictures of the Earth, like those used in satellites, capture sunlight reflected off the surface.
- Active Remote Sensing
Synopsis: Active remote sensing illuminates the region under study using its own energy source.
As an illustration, radar systems that fire pulses and measure how long it takes for them to return can provide surface pictures.
Major Components of Remote Sensing
- Sensors: Equipment for identifying and logging energy reflected or released from the surface of the Earth.
- Platforms: These can be ground-based systems with sensors or satellites, aircraft, drones, or other vehicles.
- Data processing: To glean insightful information, the gathered data is processed and examined, sometimes with the use of computer software.
Uses of Remote Sensing
- Environmental Monitoring
Assists in monitoring changes to wildlife habitats, waterways, and forests in order to safeguard the environment.
- Agriculture
To keep an eye on crop health, soil conditions, and moisture levels, farmers employ remote sensing. They can make more informed decisions and get higher yields thanks to this technology.
3. Urban Planning
Using data from remote sensing, city planners examine traffic patterns, infrastructure development, and land use to create smarter cities.
- Disaster Management
- In the event of seismic activity or floods, remote sensing provides vital information for search and rescue efforts.
The Importance of Remote Sensing
- Global Perspective: Addressing climate change and other global concerns requires the ability to observe and evaluate changes on a global scale, which is made possible by remote sensing.
- Cost-Effective: Obtaining data from space is frequently less expensive than doing it on the ground, particularly in expansive or difficult-to-access locations.
- Time Efficiency: Real-time data from remote sensing can help with quick decision-making in an emergency.
Challenges in Remote Sensing
- Data Accuracy: Depending on the sensor, resolution, and atmospheric conditions, the data quality can change.
- Technical Skills: It is common to need certain knowledge and abilities in both science and technology to analyze data from remote sensing.
- Cost of Technology: Although satellite data is becoming more widely accessible, the cost of
building and launching remote sensing satellites can be high.
What's Your Reaction?