MINERAL AND GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION
Learn about the applications of remote sensing in mineral and groundwater exploration, including spectral analysis and image interpretation.

Mineral and Groundwater Exploration
Introduction
- Remote sensing, the art of gathering information about the Earth's surface without physical contact, has revolutionized how we explore and manage our planet's resources.
- In the realm of mineral and groundwater exploration, remote sensing techniques are proving invaluable, offering a cost-effective and efficient way to identify potential resource deposits and assess their feasibility.
Remote Sensing Tools for Mineral Exploration
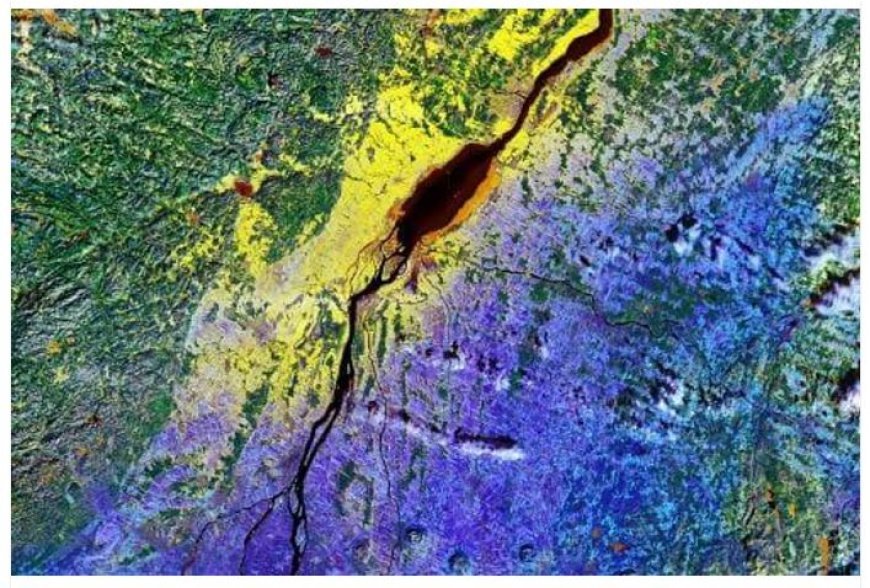
- Hyperspectral Imaging: This powerful technique captures images across a wide range of wavelengths, revealing subtle variations in mineral composition.
- By analyzing these spectral signatures, geologists can identify specific minerals associated with ore deposits.
- Multispectral Imagery: Using multiple bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, multispectral imagery can detect variations in vegetation, soil, and rock types, providing insights into geological structures and potential mineral occurrences.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR emits laser pulses to map the Earth's surface with high precision, revealing topographic features and geological structures crucial for mineral exploration.
- Radar: Penetrating clouds and vegetation, radar imagery offers valuable information about geological formations and structures buried beneath the surface.
Remote Sensing Applications in Groundwater Exploration
Aquifer Mapping: Remote sensing can identify areas with permeable rocks and sediments, indicating potential aquifer zones.
Aquifer Recharge Assessment: By analyzing vegetation patterns and soil moisture, remote sensing can assess the amount of water replenishing aquifers.
Groundwater Monitoring: Time-series analysis of satellite imagery can track changes in groundwater levels over time, providing early warning of depletion or contamination.
Salinity Mapping: Remote sensing can detect variations in soil salinity, which can indicate the presence of saline groundwater and potential contamination risks.
Benefits of Remote Sensing in Mineral and Groundwater
Exploration
Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional survey methods, remote sensing offers significant cost savings by reducing field work and logistics.
Time-Efficient: Large areas can be surveyed quickly and efficiently, accelerating the exploration process.
Environmentally Friendly: Remote sensing minimizes environmental impact by reducing the need for intrusive exploration techniques.
Enhanced Accuracy: Remote sensing data provides detailed information, improving the accuracy of resource estimations and decision-making.
Challenges and Future Trends
- Data Processing: Large datasets from multiple sources require specialized software and expertise for analysis.
- Accuracy Limitations: Some remote sensing techniques are not always able to penetrate dense vegetation or deep geological formations.
- Integration with Other Data: Combining remote sensing data with ground-based surveys and laboratory analyses is crucial for comprehensive resource assessment.
- The future of remote sensing in mineral and groundwater exploration is promising, with advancements in:
- Higher-resolution sensors: Providing more detailed information and improved accuracy.
- Integration with other technologies: Combining remote sensing with drones, geophysics, and other tools for comprehensive exploration.
What's Your Reaction?