DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
Understand the principles and techniques of digital image processing in remote sensing, including image enhancement, restoration, and classification.
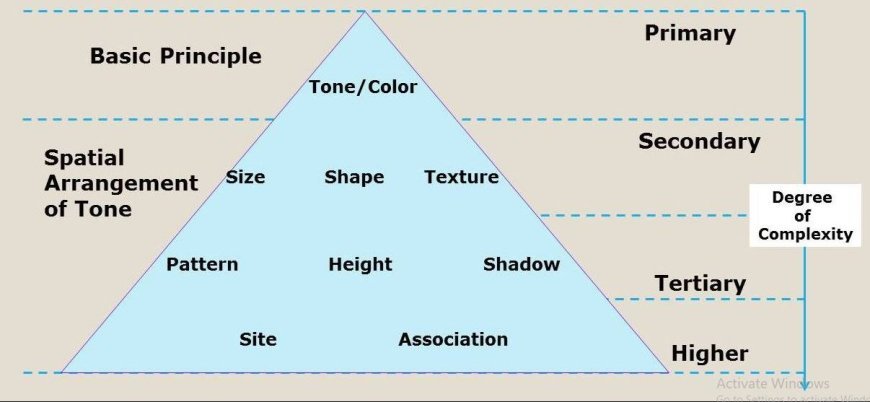
Digital Image Processing
- Remote sensing relies heavily on digital image processing, which uses advanced computer algorithms to enhance, analyze, and interpret pictures.
- These approaches are critical for increasing picture quality and extracting useful information from remote sensing data.
- The following section presents an organized overview of important digital image processing technologies.
Key Techniques for Digital Image Processing
Enhancement of Images
- Enhancement methods are used to increase the visual quality and clarity of features in remote sensing photographs. This includes:
- Contrast Adjustment: Histogram equalization is a method for adjusting an image's contrast by dispersing pixel intensity values.
- This approach improves the visibility of details, especially in photographs with low contrast.
- Brightness Modification: Changing the brightness of a picture can increase the visibility of certain aspects by rectifying difficulties where some parts are either too dark or too bright, allowing for clearer analysis.
Spatial Filtering
- Spatial filtering algorithms improve image quality by decreasing noise and emphasizing key details. These approaches include the following:
- Smoothing Filters: Filters such as Gaussian filters are used to minimize picture noise and smooth variations, therefore clarifying details and reducing distortions.
- In order to find and highlight the edges and boundaries in a picture, techniques like Sobel and Laplacian filters are used.
- This helps differentiate and delineate separate characteristics by emphasizing transitions between sections.
Transformations of Images
Picture transformation methods change picture data to allow for more thorough analysis.
Key transitions include:
- Fourier Transform: This approach transfers picture data from the spatial domain to the frequency domain, allowing for the study of periodic patterns and the use of frequency-based filters to enhance or suppress certain characteristics.
- Wavelet Transform: This approach enables multi-resolution analysis by evaluating visual data at different sizes and degrees of detail.
- It is effective for recognizing features with varying resolutions and degrees of detail.
Classification and Segmentation
- Different sections of a picture are identified and defined using classification and segmentation algorithms. This includes:
- Supervised Classification: This approach involves training algorithms with samples of known land cover categories.
- The system then classifies the remaining visual data using these specified categories.
- Unsupervised Classification: This method includes categorizing pixels based on their intrinsic qualities without prior knowledge of land cover type.
- K-means clustering is a technique for identifying natural groups in data.
Radiometric Corrections
Radiometric corrections are used to compensate for picture distortions and variances. These corrections include:
Atmospheric Correction
- The picture data is adjusted to account for atmospheric factors such as scattering and absorption, ensuring that it properly represents the Earth's surface.
- Sensor Calibration is the process of correcting sensor-related distortions and inconsistencies in order to preserve data accuracy and consistency across various sensors and imaging settings.
What's Your Reaction?