VISUAL INTERPRETATION
Learn about the visual interpretation strategies used in remote sensing, including image analysis and feature recognition.
Visual Interpretation Strategies
- Visual interpretation is a key method in remote sensing, whereby analysts scrutinize pictures to discern and evaluate elements based on their visual characteristics.
- This strategy continues to be a fundamental approach because of its straightforwardness and efficiency.
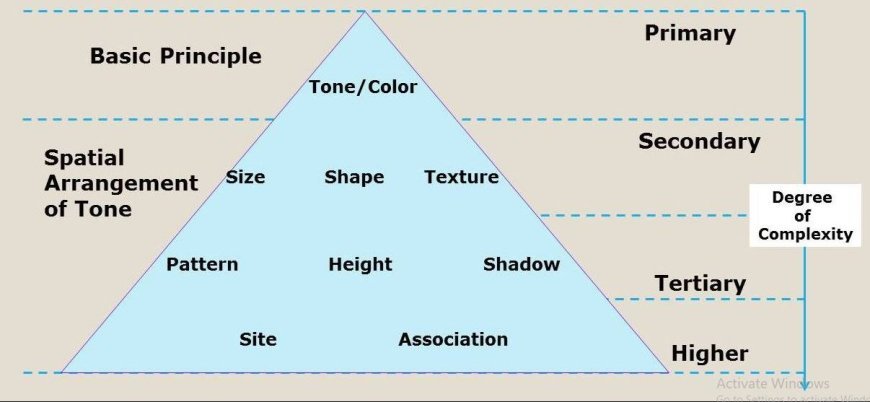
- Presented here is a thorough examination of visual interpretation processes, characterized by relevant aspects.
Key Approaches for Visual Analysis
Analysis of Color
- Color analysis entails the examination of color changes in remote sensing photographs in order to differentiate between various features and types of land cover.
These items are comprised of:
- Color composites, such as false-color photographs, improve the capacity to distinguish between different forms of land cover.
- Specific color schemes can be used to highlight the distinct spectral qualities of vegetation and water bodies, making it easier to distinguish between them.
- Spectral bands refer to specific ranges of wavelengths at which different materials reflect light. Through the examination of these spectral bands, it is possible to determine and categorize different types of land cover by their distinct colors and patterns of reflection.
Analysis of texture
- Texture analysis is a method that examines the surface characteristics of objects in a picture to get understanding of their physical attributes and how the land is being used. This includes:
- Surface roughness refers to the process of assessing the texture of a surface in order to determine its level of roughness or smoothness.
- For instance, regions with a high density of vegetation, such as forests, display distinct textural patterns in contrast to metropolitan areas or bodies of water.
- Pattern recognition involves the identification of certain patterns in the texture that are associated with various types of land cover.
- This aids in comprehending land-use patterns and differentiating between different surface types.
Shape and pattern recognition
- Identifying and classifying aspects in a picture is facilitated by the ability to recognize forms and patterns, which is done by analyzing their geometric qualities.
The following items are included:
- Geometric patterns: Examining unique geometric patterns or arrangements, such road networks or building layouts, can determine the presence of man-made structures or land use categories.
Spatial arrangement
- Spatial arrangement refers to the evaluation of how characteristics, such as groups of plants or patterns of urban growth, are organized and distributed throughout a certain area.
- This assessment helps in understanding the types of land cover and their distribution.
Contextual interpretation
- Contextual interpretation refers to the process of analyzing and understanding a work or piece of information by considering its surrounding context, such as the historical, cultural, or social factors that may influence its meaning.
- Contextual interpretation is analyzing the immediate surroundings and the connections between different elements to improve comprehension. The following items are included:
- Surrounding Features: Analyzing characteristics in connection with their immediate surroundings.
- For instance, the identification of agricultural fields in connection to proximate water sources or metropolitan areas might yield valuable insights regarding land use and management techniques.
- Historical Knowledge: Utilizing preexisting knowledge of the region and past data to assist in the analysis of present photos.
- This facilitates the identification of alterations and comprehension of the circumstances surrounding observable characteristics.
What's Your Reaction?