IMAGE RECTIFICATION AND RESTORATION
Learn about image rectification and restoration techniques in digital image processing, including geometric correction and radiometric correction.
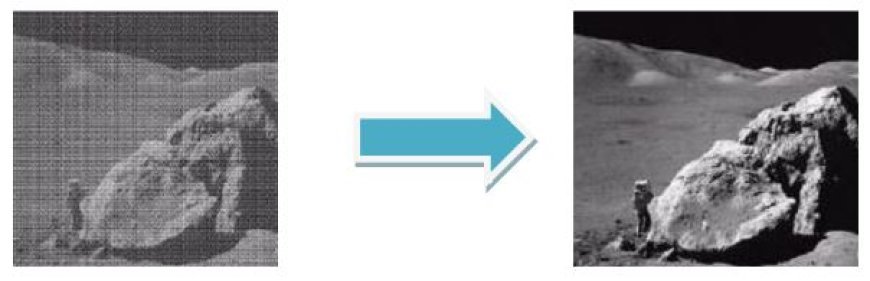
Image Rectification and Restoration
- Image rectification and restoration are two separate but interconnected procedures in the field of image processing that seek to enhance the quality and usefulness of digital photographs.
- Both of these approaches are indispensable in a wide range of applications, including photography, satellite images, medical imaging, and computer vision.
Image Rectification
Rectification of an image
- Picture rectification is the procedure of correcting geometric defects in a picture to get a more precise depiction of the real-world situation.
- The process entails converting the picture from a perspective view to an orthographic projection, in which parallel lines in the scene are depicted as parallel in the image.
- This is especially crucial for applications that need accurate spatial measurements or for merging photos captured from various perspectives.
- The purpose of this is: The primary goal of image rectification is to mitigate the impact of lens distortion, camera tilt, and perspective, which can affect the perceived locations of objects inside an image.
- Rectifying a picture simplifies tasks such as feature matching, 3D reconstruction, and change detection.
Steps
1. Distortion Identification: Analyze the image to identify the specific forms of geometric distortions, such as radial distortion, tangential distortion, and perspective distortion.
2. Camera Parameter Estimation: Determine the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of the camera, including focal length, primary point, and orientation angles. These characteristics are crucial for comprehending how the camera recorded the picture.
3. Correction Model: Select a suitable model, such as the pinhole camera model, fisheye model, or radial distortion model, to rectify the distortions.
4. Parameter Estimation: Utilize the recognized forms of distortion and the selected correction model to accurately determine the particular parameters required to repair the image.
5. Picture Transformation: Utilize the estimated parameters to apply the rectification transformation to the original picture, resulting in an image that is free from distortion.
6. Resampling: The corrected picture may have different pixel sizes as a result of the transformation. Perform picture resampling to generate a grid of pixels that are evenly spaced.
Applications
- Photogrammetry is a technique used to obtain precise 3D models and data from aerial or satellite photographs.
- Augmented Reality refers to the process of superimposing digital information onto the physical environment in a way that does not cause any distortion.
- Panorama Stitching is the process of merging numerous photos taken from different perspectives into a single, uninterrupted panoramic image.
Image restoration
- Definition: Image restoration refers to the procedure of recreating a pristine, superior image from a deteriorated one.
- Picture restoration include the elimination of noise, blur, and other imperfections that may have been introduced during the process of capturing or transmitting the picture.
- The purpose: The objective of image restoration is to improve the visual fidelity of pictures and recover the original data that was lost or damaged.
- This is crucial in situations where the sharpness of a picture can have a substantial impact on decision-making, such as in medical diagnosis or forensic investigation.
Steps
1. Degradation Modeling: Analyze the specific form of degradation that is affecting the
image, such as noise, blur, or compression.
2. Noise Reduction: Implement algorithms such as Gaussian filtering, median filtering, or wavelet-based approaches to diminish random noise.
3. Deblurring: Utilize deconvolution methodologies to counteract the consequences of blur, which may arise from camera movement or defocusing.
4. Inpainting: Using data from neighboring pixels, fill in areas of the image that are missing or damaged.
5. Enhancement: Modify the contrast, brightness, and other picture attributes to enhance visibility and enhance the level of detail.
6. Output: Produce the reconstructed image, aiming for maximum similarity to the original, unimpaired image.
Applications
Medical Imaging: To optimize picture quality for improved diagnostic accuracy.
Historical Document Preservation: The process of repairing and rejuvenating deteriorated or old photographs and records.
Forensic Analysis: Enhancing the visual clarity of surveillance or crime scene photographs.
Satellite and Aerial Imagery: Used to restore the original features that are hidden due to atmospheric conditions or sensor noise.
What's Your Reaction?