TSUNAMI
Tsunamis reshape landscapes, leaving a lasting geological mark.
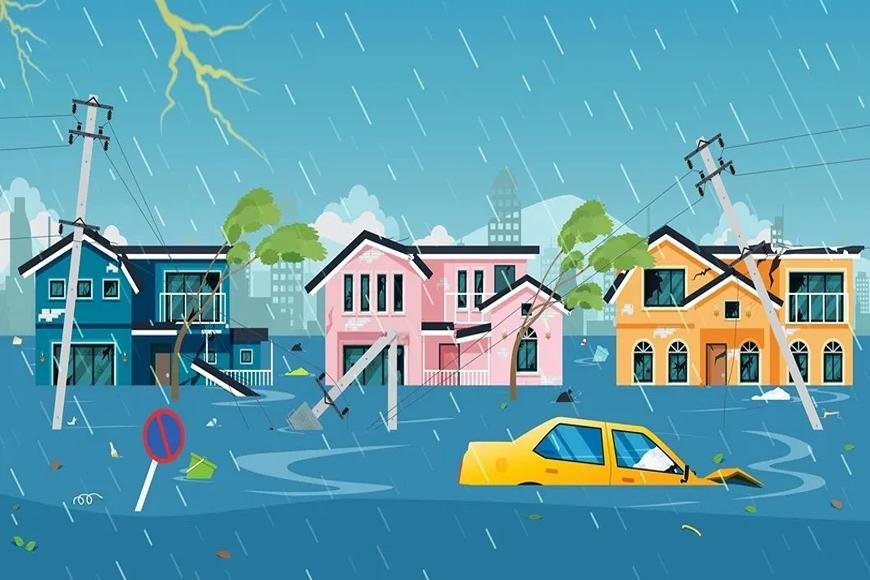

Tsunami
- The meaning of a tsunami says that it is "a set of waves caused by the movement of a large body of water in a body of water, usually an ocean or a large lake.
- " Since the word "tsunami" means "wave," we can also call these things "tidal waves."
- Both tsunamis and tides move water inland, but the movement of water inland during a tsunami can be much greater, making what looks like a very high and strong tide called a tsunami wave.
OCCURRENCE OF TSUNAMI
- Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, detonations, landslides, glacier calving, meteorite strikes, and other man-made issues in or above the water can all cause tsunamis.
- The movement of a sizable amount of water or waves in the ocean is what primarily causes a tsunami.
- Earthquakes, landslides, volcanic eruptions, ice breaking off, and, less frequently, meteorites and nuclear tests can all result in the movement of water.
- Tsunamis happen all over the world because of earthquakes.
Let's look at a more in-depth description of what causes tsunamis.
- The earthquake that sets off tsunamis can happen when the bottom quickly changes shape and moves the water above it up and down.
- A tectonic earthquake is a type of earthquake that happens when the ground beneath us moves. When these kinds of earthquakes happen under the water, the water above the area that is damaged moves out of its normal state.
- A tsunami can happen when thrust faults connected to convergent or damaging plate boundaries move quickly, moving water. This is possible because of the vertical component of movement.
- Tsunamis don't make a lot of noise at sea because their waves are low and have a long range. They only make a small swell about 300 mm (12 in) above regular sea level.
- When they get to shallow water, the waves shoal, which makes them taller. A tsunami can happen at any level of the tide, and even at low tide, seaside places can be flooded.
- The tsunami was caused by weather conditions.
- Weather changes are the cause of meteorological tsunamis.
- Barometric pressure can change quickly, like when a front goes through. This can move bodies of water around enough to create waves with wavelengths similar to those of tsunamis but less energy.
- These are basically dynamically similar to seismic tsunamis, but meteor tsunamis don't happen across oceans like big seismic tsunamis do, and the force that moves the water around stays the same over time, so they can't be modeled as happening quickly.
- Even though they have lower energies, they can still be strong enough to damage and kill people near the shore, where resonance can make them stronger.
Types of Tsunami
- There are three main types of tsunamis that happen all over the world. Let's talk about the different kinds of tsunamis in this piece.
Local Tsunami
- As the name suggests, a local tsunami is one that does damage close to the event that caused it.
- The watery event, which is usually an earthquake that sets off a small tsunami, happens less than 100 kilometers (about 60 miles) from the damage on land.
- It can be less than an hour or even less than 10 minutes between the underwater event and the arrival of the tsunami. This means that these tsunamis can be very bad.
- Not enough time has been given to make a full escape.
Regional Tsunami
- Any tsunami that does damage between 100 and 1,000 kilometers from where it started is called a regional tsunami. Damage will sometimes be less severe outside the 1,000-kilometer limit.
- Regional tsunamis arrive between one and three hours after the event that caused them, which is a lot longer than local tsunamis.
- One to three hours might not be enough time for people to easily leave a 1,000-kilometer radius.
Distant Tsunami
- A faraway tsunami, also called a Tele tsunami or ocean-wide tsunami, is caused by something very powerful that happens more than 1,000 kilometers from where it hits land.
- A tsunami from far away might look like a tsunami in your area at first, but it covers a huge area of the ocean basin.
- A tsunami that is far away gives people more time to get out of harm's way, but it also covers more land and is more likely to do a lot of damage all over.
What's Your Reaction?