STRATIGRAPHIC TERMINOLOGY, NOMENCLATURE AND CLASSIFICATION
Learn about the standardized terminology, nomenclature, and classification used in stratigraphy to describe rock layers. Understand the importance of clear communication in geological sciences.
AN OVERVIEW OF STRATIGRAPHIC TERMINOLOGY, NOMENCLATURE, AND CLASSIFICATION
- A key discipline of geology, stratigraphy is the examination of the order, age, and relationship of rock strata.
- The establishment of a uniform system of vocabulary, nomenclature, and categorization is crucial for the efficient communication and comprehension of geological formations.
- Stratigraphic Unit: A rock body owning unique features that enable its mapping and description as a cohesive entity.
- A lithostratigraphic unit is a unit described by its lithological features, such as rock type, color, and texture.
- A biostratigraphic unit is a unit that is determined by its fossil richness.
Chronostratigraphic Unit: A unit determined by its age using absolute dating methods. - A Time-Stratigraphic Unit is a geometric unit that represents a precise period of geological time.
Lexical Terms
- Stratigraphic units are named according to particular rules in order to guarantee clarity and uniformity.
- Stratigraphic units are often designated based on a geographical position, a unique attribute, or a geological process. For instance:
- Classification of lithostratigraphic units: Sandstone Formation, Limestone Member
- Taxonomic units: Ammonite Zone, Dinosaur Bed
- Chronostratigraphic units: Eocene Epoch, Cretaceous Period
Taxonomy
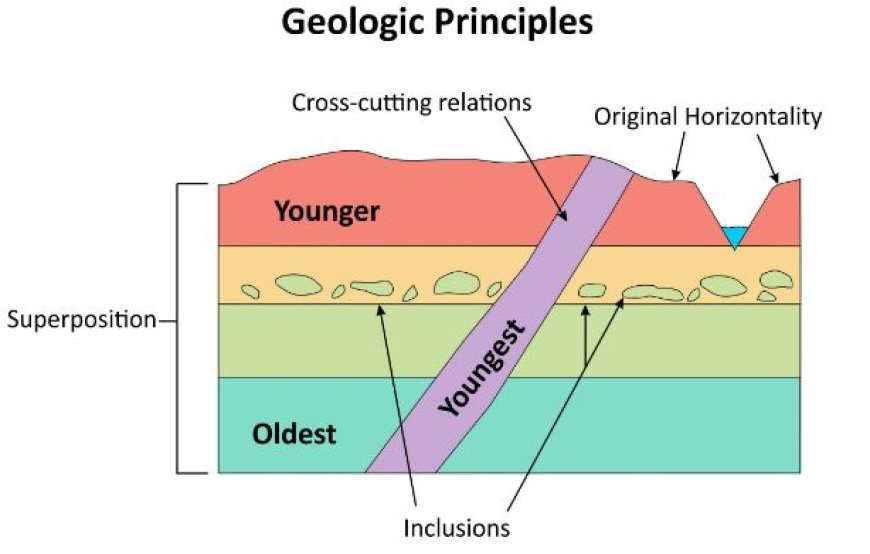
- Stratigraphic units can be categorized according to their comparative age and vertical location. Principal categorization systems consist of:
- The concept of superposition states that younger rocks are placed on top of older rocks, provided that no major disruption has taken place.
Cross-Cutting Relationships: A geological structure that intersects another is often of a more recent age.
Rock pieces that are incorporated within another rock are of a much older age than the host rock.
Unconformities are gaps in the geological record that indicate historical periods of erosion or lack of deposition.
Stratigraphic Correlations
- Effective correlation of stratigraphic units from several places is essential for comprehending the geological history of a broader area. This entails the identification of common features, such as lithology, fossil fossils, and age correlations. Some methods employed for correlation analysis are:
- The lithostratigraphic correlation is established by comparing rock types and their sequences.
- Biostratigraphic correlation is determined by the existence and spatial arrangement of fossil remains.
- Chronostratigraphic correlation is established using absolute age measurements.
Additional Considerations
- Facies refer to the horizontal separation of rock groups caused by changes in the conditions under which they were deposited.
- Correlation charts are graphical depictions of associations and connections among stratigraphic features.
- Codes for Stratigraphic Nomenclature: Global recommendations and benchmarks for stratigraphic nomenclature.
What's Your Reaction?