ENERGY CIRCULATION AND HUMAN RISK IN ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY
Discover how internal and external energy sources shape our environment, from plate tectonics to solar radiation.
A Comprehensive Analysis of Energy Circulation and Human Risk in Environmental Geology
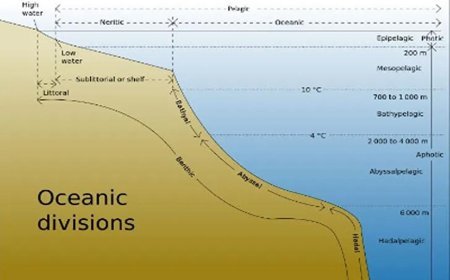
- Environmental geology is an interdisciplinary discipline that integrates concepts from geology, biology, chemistry, and physics to comprehend the dynamic processes of the Earth, the ecological consequences of human actions, and the possible hazards to human existence.
- Fundamental to this discipline is energy circulation, which includes the transfer, conversion, and application of energy throughout the systems of the Earth.
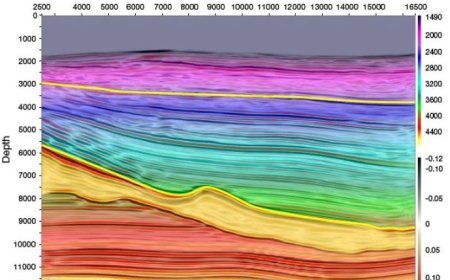
Energy circulation
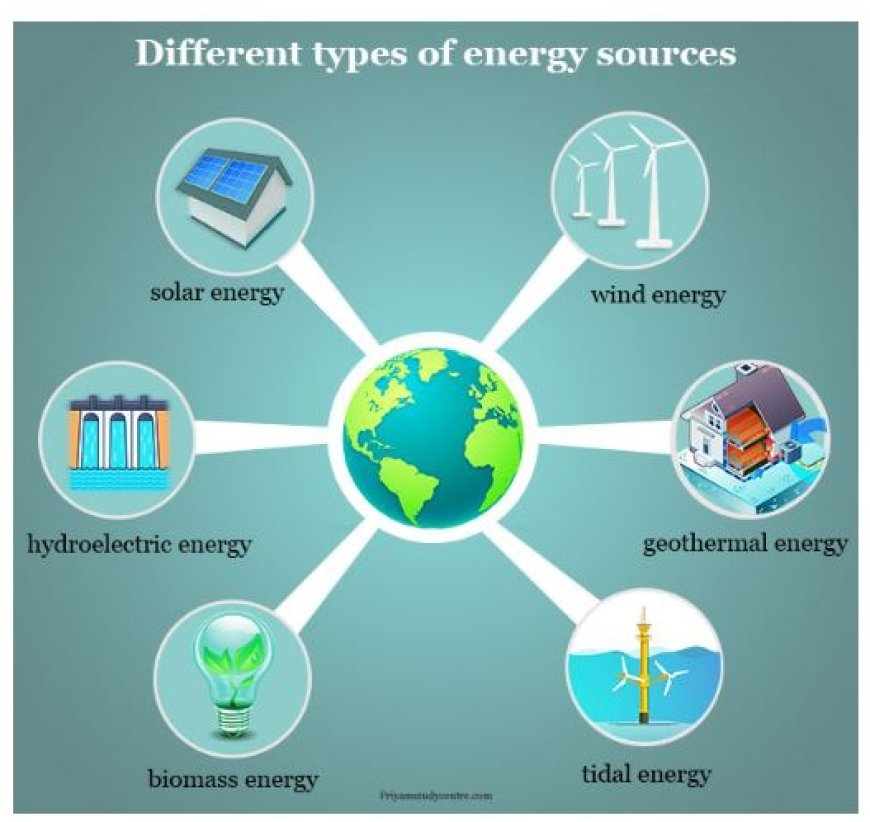
- Energy circulation is a dynamic phenomenon including distinct types of energy such as solar radiation, geothermal heat, mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy.
- The aforementioned energy sources are harnessed and optimized by means such as photosynthesis, volcanic activity, wind, hydropower, and nuclear reactions.
- An essential function of energy circulation is to sustain the Earth's temperature and biogeochemical cycles, therefore ensuring the survival of life on our planet.
Analysis of Human Risk: Origins and Consequences
- A wide range of dangers and hazards can result from the substantial influence of human activities on energy circulation patterns.
- An exemplary illustration of this phenomenon is the burning of fossil fuels, which significantly contributes to global warming, air pollution, and the disturbance of ecosystems.
- Furthermore, the extraction of fossil fuels through mining and drilling activities can result in soil erosion, damage to habitats, and contamination of water.
- The extraction of geothermal energy, although providing a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy option, can also provide hazards.
- For example, the process of geothermal drilling has the potential to induce seismic activity and emit hazardous contaminants, including hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide.
- Moreover, the building of dams for hydropower can result in substantial environmental modifications and hazards, such as modifications in the local drainage patterns, depletion of aquatic ecosystems, and heightened vulnerability to seismic activity.
An Examination of the Function of Environmental Geology in Risk Mitigation
- The mitigation of these threats is a crucial responsibility undertaken by environmental geologists.
- The identification of possible dangers and vulnerabilities linked to energy production and consumption may be achieved via the study of local and regional geology.
- This includes the execution of geological surveys, the surveillance of seismic activity, and the evaluation of water resources and soil stability.
- Furthermore, environmental geologists make a substantial contribution to the development and execution of sustainable energy strategies.
- They can make recommendations for the placement of wind and solar farms, considering factors such as wind patterns, sun intensity, and the possible effects on nearby ecosystems.
- Their expertise extends to providing guidance on the execution of geothermal energy initiatives, therefore guaranteeing little disturbance to nearby populations and ecosystems.
What's Your Reaction?