DRAINAGE SYSTEM
Rock & water, a powerful duo! Drainage systems link geology and hydrology, shaping Earth's story.
DRAINAGE SYSTEM
- Moving water through clear channels is called drainage, and the network of these channels is called a "drainage system."
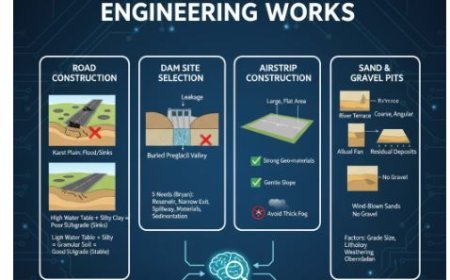
- Geological time periods, rock type and structure, topography, slope, the amount of water flow, and how frequently it occurs all affect the drainage system of a given area.
- The drainage basin of a single river system is known as its drainage basin, while the "Water Divide" is an elevated region that divides two drainage basins.
- Here are some key phrases to know when it comes to drainage and drainage systems:
- The geological time period, rock type and structure, topography, slope, and other elements all have an impact on an area's drainage pattern.
- A river drain is a defined area inside the river's catchment basin.
- A drainage basin is a region that a river and its tributaries drain.
- The watershed area is the boundary that divides one drainage basin from another.
- When water bodies join together, they are referred to as tributaries.
- A distributary is a river that flows from another river.
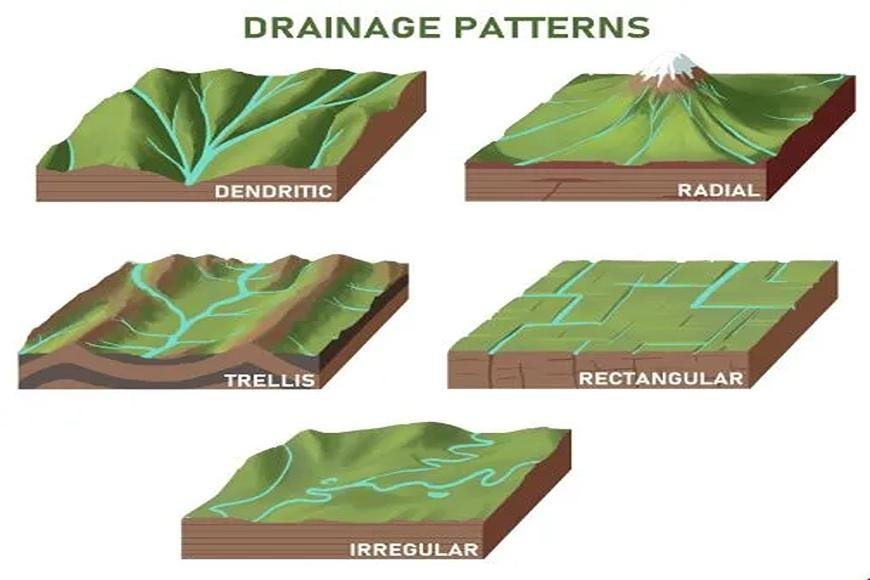
Types of Drainage Patterns
The principal drainage patterns are as follows:
Dendritic
- Dendritic patterns show up where river routes follow the sloping terrain.
- The creek and its tributaries are named Dendritic because they resemble tree branches.
- For example, the rivers of the northern plains, such as the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra,.
Trellis
- When a river and its small streams join together almost at right angles, they make a crisscross design. trellis-like design. Hard and soft rocks coexist in parallel, providing a trellis drainage pattern.
- For example, the rivers of the higher Himalayan area, such as the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra.
Rectangle
- A rectangle drainage pattern occurs on a firmly joined rocky surface.
- Streams found in the Vindhya mountain range, for example, are Chambal, Betwa, and Ken.
Radial
- A radial pattern appears when a watercourse travels in various directions from a central peak or dome-like structure.
- For example, the Narmada and Son rivers originate in the Amarkantak range.
Parallel
- It develops in regions with parallel, elongated landforms and a substantial surface slope.
- Tributary streams tend to stretch out in a parallel-like manner as they follow the slope of the surface. Godavari, Kaveri, Krishna, and Tungabhadra rivers, for example, originate in the Western Ghats.
Centripetal
- The polar opposite of the radial, as streams flow towards a central depression.
- These streams feed ephemeral lakes, which evaporate during dry spells throughout the year. For example, Loktak Lake.
What's Your Reaction?