SOIL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION
Learn about the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soils and how they are classified.
Properties and Classification of Soils
- Earth's surface is covered in a thin layer of substance called soil, yet soil is much more than simply dirt.
- With a complex interaction of physical, chemical, and biological qualities that sustain life, it is a dynamic, living system.
- Agriculture, forestry, and environmental management all depend on understanding these characteristics.
Physical Characteristics: Soil Components
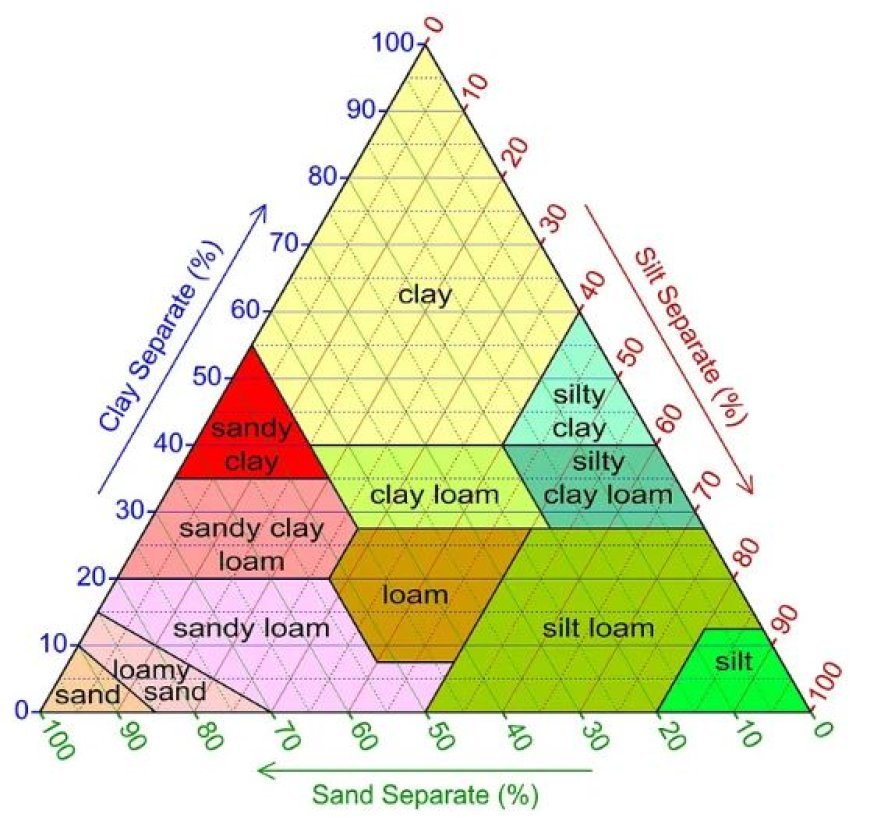
- A soil's feel and capacity to retain water and nutrients are determined by its texture, which is determined by the proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
- Large-particle sand soils drain fast but are low in nutrients.
- Although they are made up of small particles, clay soils can compress but still hold onto water and nutrients.
- Particle size in silt soils is medium, providing a balance between nutrient retention and drainage.
- Aeration, root development, and water infiltration are all influenced by soil structure, or how the particles are arranged into aggregates.
- Because they are crumbly and permeable, well-structured soils promote the growth of healthy plants.
- The weight of soil per unit volume, or soil density, has an impact on aeration and root penetration.
Chemical Characteristics
- The acidity or alkalinity of the soil, or pH, determines what nutrients are available to plants.
- Plants are able to absorb necessary components such as potassium, phosphate, and nitrogen when the pH range is balanced.
- The decomposing remnants of plants and animals, or organic matter, nourish the soil with nutrients, increase its ability to hold onto water, and improve its structure.
- For a healthy soil ecosystem to function, soil organic matter is essential.
- Minerals that are necessary for plant development, such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, are incorporated into the soil through weathering and decomposition.
The Living Soil's Biological Properties
- Numerous organisms, such as fungus, bacteria, and insects, are abundant in soil and contribute to its overall health.
- Organic matter is broken down by microorganisms, which releases nutrients and enhances soil structure.
- Earthworms are an essential part of the soil ecology because they mix organic debris, promote drainage, and aerate the soil.
- This complex biological process affects the fertility of the soil, the cycling of nutrients, and the general health of the ecosystem.
Categorising the Variable Soils on Earth
- Systems for classifying soils systematically allow for the grouping of soils according to their properties, such as organic matter concentration, structure, texture, and profile development.
- Based on their major qualities, soils are grouped into 12 orders under the United States Department of Agriculture's (USDA) hierarchical Soil Taxonomy system.
- To create a comprehensive categorisation system, these orders are further split into suborders, large groupings, subgroups, families, and series.
- Scientists can forecast soil behaviour, efficiently manage resources, and provide specialised solutions for particular problems by having a solid understanding of soil categorisation.
What's Your Reaction?