SOIL EROSION CAUSES, CONSEQUENCES AND CONSERVATION STRATEGIES
Explore the causes and effects of soil erosion, including water and wind erosion, and learn about strategies for prevention and remediation.
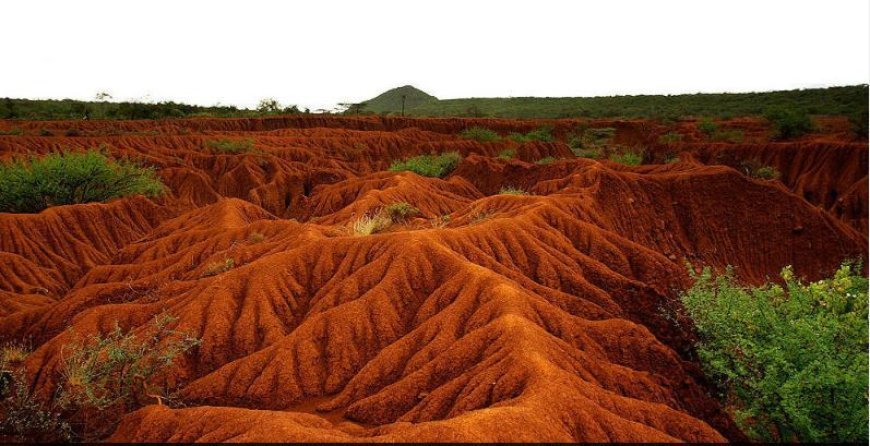

Soil Erosion: Causes, Consequences and Conservation Strategies
- Soil erosion is a complicated natural problem with many sides that impacts forests, farming, and human cities all over the world.
- Soil degradation happens over time, taking away rich land, making farming less productive, and raising the risk of natural disasters.
- Understanding what causes soil loss and what effects it has is important for coming up with good ways to lessen its effects.
Causes of Soil Erosion
- Loss of trees and changes in land use
- Soil loss happens when woods and other wild plants are cut down to make room for farming, cities, and new infrastructure.
- Getting rid of trees and other plants that help hold the earth in place makes the soil more likely to sink or become unstable.
2. Practices of intensive farming
- Over-tilling, monoculture farming, and not switching crops all the time damage the soil and make it more likely to wash away.
- These actions change the structure of the soil, remove organic matter, and make the soil more dense.
- Changes in the climate
- Soil loss is made worse by changes in the way it rains, more extreme weather events, and higher temperatures.
- The amount of water in the soil changes when it gets warmer, which makes
- it more likely to wash away.
4. Bad management of the land
Erosion is made worse by not protecting the soil properly, like not using terracing, contour farming, or buffer strips. Inadequate land management practices lead to increased soil exposure and erosion.
5. Overgrazing
- Too much cattle feeding compacts the earth, making it less able to hold water and raising the risk of flooding.
- Also, overgrazing removes plants from the land, making it more likely for dirt to
- wash away.
6. Population Growth and Urbanization
As cities grow and more people move into them, farming land grows, infrastructure is built, and more resources are needed, which causes soil loss.
7. People don't know how to protect soil.
People who don't know enough about or understand the effects of soil loss don't do enough to stop it, which makes the problem worse.
Consequences of Soil Erosion
- The Loss of Farmable Land
Soil loss makes farms less productive, which hurts food security and local businesses. Crops need fertile land to grow, and when it's lost, food supplies drop.
- Pollution of water
Soil erosion causes sediment and nutrients to run off into areas of water, which hurts marine species. Polluted water is bad for people, animals, and the earth.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions
Erosion of the soil released carbon that has been stored in the air, which makes climate change worse. Keeping carbon in the soil is a key part of slowing down climate change.
- Infrastructure Damage
Landslides, floods, and infrastructure destruction may all result from soil erosion. Damage to infrastructure slows down the economy and changes where people live.
- Biodiversity loss
Ecosystems are changed by soil loss, which puts at risk plant and animal species that depend on certain soil conditions. Loss of biodiversity affects the benefits and stability of ecosystems.
- Lack of food security
Soil loss lowers crop output, which affects the price and supply of food, especially in areas that are already struggling. People's health and well-being are affected by not having enough food.
- Effects on the economy
The farm, forestry, and tourist businesses all lose a lot of money because of soil erosion. Local and national economies are both affected by economic effects.
8. Social Impacts
Soil loss changes where people live, which can cause movement, displacement, and social unrest. The well-being and togetherness of a group are affected by social effects.
Plans for protecting nature
- Planning for sustainable land use
The chance of soil runoff goes down when sensible land-use methods like agroforestry and permaculture are used.
2. Ways to protect the soil
Soil runoff can be stopped by terracing, contour farming, and buffer strips. The dirt stays in place, and there is less waste with these methods.
3. Planting trees and replanting trees
Restoring wood and planting trees help keep the land healthy, stop runoff, and encourage wildlife.
4. Managing the fertility of the soil
Conservation agriculture methods, like crop rotation and adding organic matter to the soil, make it more fertile and lower the risk of flooding.
5. Steps to Stop Erosion
Using erosion control tools like riprap and geotextiles lowers the risk of soil loss in important places.
6. Getting involved in and aware of the community
To handle soil well, people need to know more about the effects of soil loss and be encouraged to take part in protection activities.
7. Frameworks for policies and laws
Soil loss can be stopped by making and following laws and policies that support soil protection and healthy land-use practices.
What's Your Reaction?