RIVER FLOODING CAUSES AND FACTORS INFLUENCING FLOOD SEVERITY
Understand the factors that contribute to river flooding, including precipitation, land use, and channel morphology.
Analysis of River Flooding: Causes and Factors Affecting Flood Severity
River Flooding
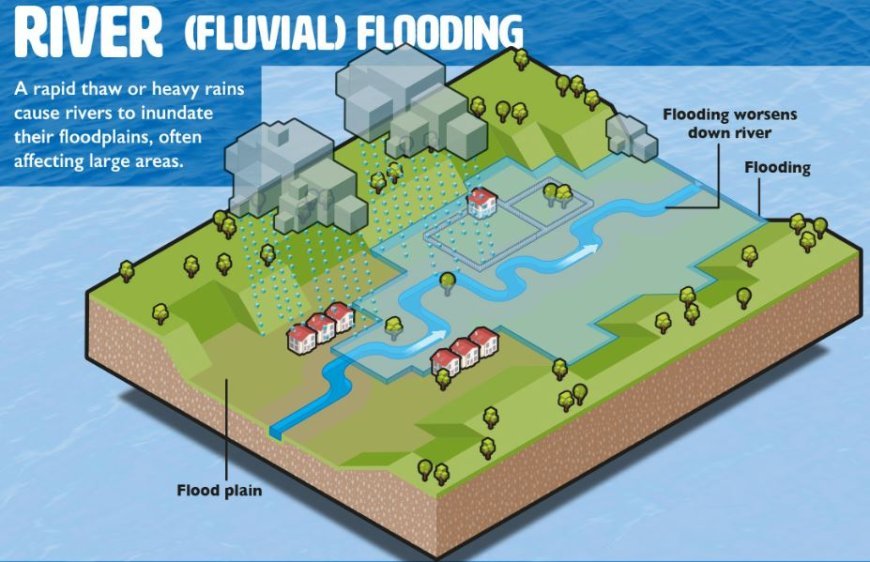
- River flooding is the phenomenon when the water levels exceed the boundaries of a river, resulting in the overflow into neighbouring geographical regions.
- The overflow may have detrimental effects on residential properties, roadways, and agricultural farmlands, resulting in devastation and disturbance.
The Significance of Investigating River Flooding
- The study of river flooding is of utmost importance for disaster preparedness since it enables communities to anticipate and effectively respond to future floods.
- Environmental Conservation: It helps safeguard ecosystems impacted by floods.
- The analysis of flood hazards may provide valuable guidance for improving land-use planning in urban areas.
Factors contributing to river flooding
- Intense precipitation
- Definition: Extended durations of intense precipitation may render the soil saturated and result in heightened river flow.
- Impact: Reduced soil absorption capacity is a prevalent factor contributing to river floods, particularly in areas with poor soil qualities.
- Snowmelt
- During the spring season, as temperatures increase, the process of snow melting may lead to a flow increase in rivers.
- Consequence: Abrupt melting from elevated regions may result in swift streamflows, triggering floods even in the absence of significant rainfall.
- Ice Jams
- Ice sheets may develop in rivers throughout the winter season and disintegrate in spring, resulting in abrupt obstructions.
- One consequence of ice barriers is the potential for localised flooding events when water flows back up behind them.
- Dam failures
- Dam failures refer to the occurrence of dam breaches caused by inadequate maintenance or natural calamities, which disrupt the management of river flow by dams.
- Consequence: An abrupt discharge of accumulated water results in very destructive floods farther downstream.
- Land Use Changes: Destruction and urbanisation might lessen the land's capacity to absorb precipitation.
- Impact: Impermeable surfaces, such as concrete, amplify hydrological discharge, resulting in elevated river levels and subsequent floods.
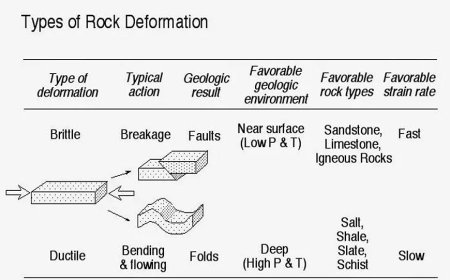
Key Determinants of Flood Severity
1. Geology of the Environment
- Soil Type and Saturation: Sandy soils have superior water absorption capabilities compared to clay soils, resulting in faster saturation.
- Land topography: Steep slopes result in rapid water flow, hence heightening the vulnerability to flooding.
2. Climate and Meteorological Patterns
- Seasonal Factors: Specific periods of the year, such as monsoon seasons, are more susceptible to intense precipitation and flash floods.
- Severe Weather Events: Hurricanes and tropical storms may provide copious rainfall that inundates river basins.
3. Human Activities
- Urban Development: Construction activities might result in a decrease in green areas, which otherwise serve as natural absorbers of rainwater.
- Agricultural techniques: Specific agricultural techniques may worsen soil erosion, resulting in higher sediment loading in rivers, therefore increasing the danger of flooding.
- Hydrological Systems
- River Systems: The dimensions and deflection capability of rivers dictate their water handling capacity prior to the occurrence of floods.
- Characteristics of Watersheds: Watersheds of greater size accumulate more precipitation and thereby result in increased flow rates.
- Vegetation Cover
- Function of Plants: Vegetation facilitates the absorption of rainwater. Environments affected by deforestation are more vulnerable to flooding.
- Plant root systems play a crucial role in soil consolidation, therefore mitigating the risk of landslides and other erosional processes that may result in heightened flooding severity.
What's Your Reaction?