QUARTERNARY PERIOD
The Quaternary witnessed dramatic climate swings and the rise of modern humans.
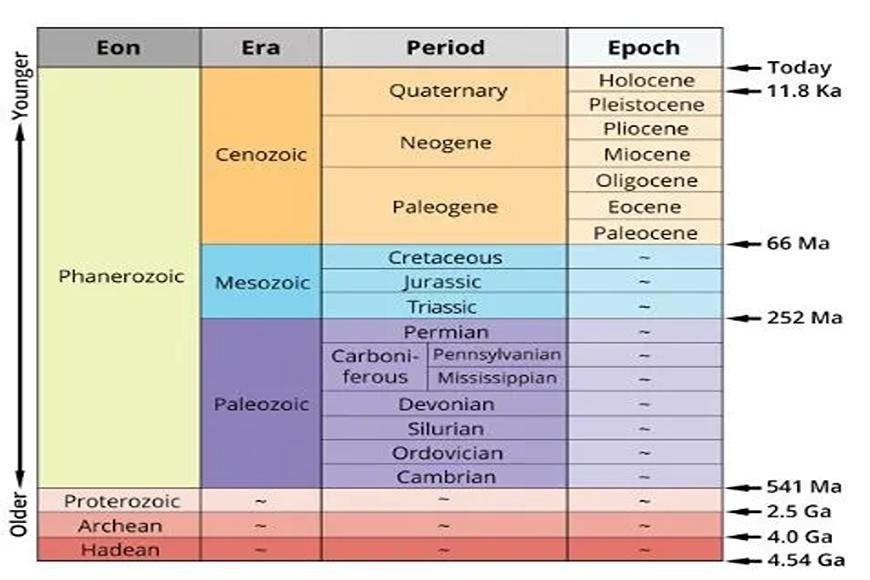
- Geological time is broken up into several parts called the Quaternary.
- Between 2.6 million years ago and now, the Quaternary Period is what we are living in. It is made up of the quaternary and tertiary periods.
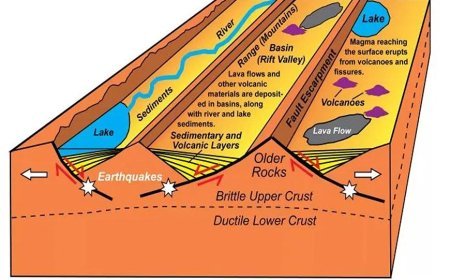
Quaternary Geography
- For example, the Pleistocene era began about 11,700 years ago and ended about the same time as the present day.
- The Holocene era began about 11,700 years ago and ended at the same time as the present day.
- People evolved a lot during the Quaternary Period, which is one of the most amazing times in the history of the Earth's climate.
- Many species have gone extinct because of the big changes in the planet's temperature that happened during the Quaternary Period.
- These changes have changed food supplies and eliminated many species.
- A man, a new type of hunter, also became more common during this time.
Climatic Conditions During the Quaternary Period
- Over the past 60 million years, scientists from all over the world have found proof of warmer times between longer periods of glacial expansion.
- Since Antarctica is still covered in ice, the whole Quaternary Period, which includes now, is called an "ice age.
- Studies, on the other hand, show that the Pleistocene Epoch was much drier and colder than currently.
- Even though glaciers moved at different rates on different continents, they covered about 30% of the earth's area about 22,000 years ago.
- Extremely large grasslands called "mammoth steppes" used to exist in what is now Europe and North America.
- They were more productive and had more biomass than current grasses. It was hard to see through the grass, but it was very healthy.
- The winter snow cover, on the other hand, was not very deep.
Rise of Mankind During the Quaternary Period
- Primitive humans, like Homo erectus, were the first to use fire in a big way.
- It is thought that the species came from one of two factors.
- According to the first theory, the species started out in Africa and then spread to Eurasia, where they were able to survive by using fire and tools to get around in colder places.
- People who believe the second theory say that Homo erectus moved to Africa from Eurasia.
- Homo erectus fossils found in Dmanisi, Republic of Georgia, show that this species was a good hunter.
- Around 200,000 to 30,000 years ago, Homo neanderthalensis lived on Earth. As far south as Gibraltar and the Levant, fossils from the species' home in western Europe showed that it lived there.
- This includes southern Great Britain, central Europe, and Ukraine. African remains of Neanderthals have not been found, though.
- Their hands and arms were longer and stronger than ours, and they were shorter and stockier than modern people.
- Building homes, making clothes, and using a variety of stone and bone tools were things they did every day.
- These people were very good at hunting because the weather meant they had to eat a lot of animal energy.
- Plants were also cooked and eaten, according to a new find.
- To honor their dead, they buried them and made things that were pretty or had meaning.
- To date, no fossils of older hominids have shown that they used language-like behaviors.
- Anatomically modern human fossils from Ethiopia, which are about 195,000 years old, show that Homo sapiens came from Africa.
- They lived in what is now Israel and other places in the north as late as 100,000 years ago.
- The oldest fossils of modern humans are also found in the north, but they are only 40,000 to 60,000 years old.
- The fact that Homo sapiens and Homo neanderthalensis lived at the same time for a while is clear from this finding.
- H. sapiens may have reached adulthood later than Neanderthals, but there isn't much tooth evidence to support this.
- As a result, kids had more time to learn how to get along with others and pass on information and technology to younger generations.
- Women and children may have been able to find more kinds of food by splitting up the work, which may have begun with this.
- When the weather got cooler again, Homo humans might have been better off if they tried eating a wider range of foods.
- Neanderthal skeletons from about 28,000 years ago are the most recent ones found.
- Unfortunately, the Neanderthals died out because of the drastic changes in temperature, but Homo sapiens survived and continued to live all over the world.
What's Your Reaction?