Instrumentation for NMR: Extra Techniques
Discover NMR instrumentation and extra techniques like MRI, DNMR, solid-state, and high-resolution NMR. Learn how magnets, RF systems, and spectrometers reveal molecular structure, motion, and biomedical insights.
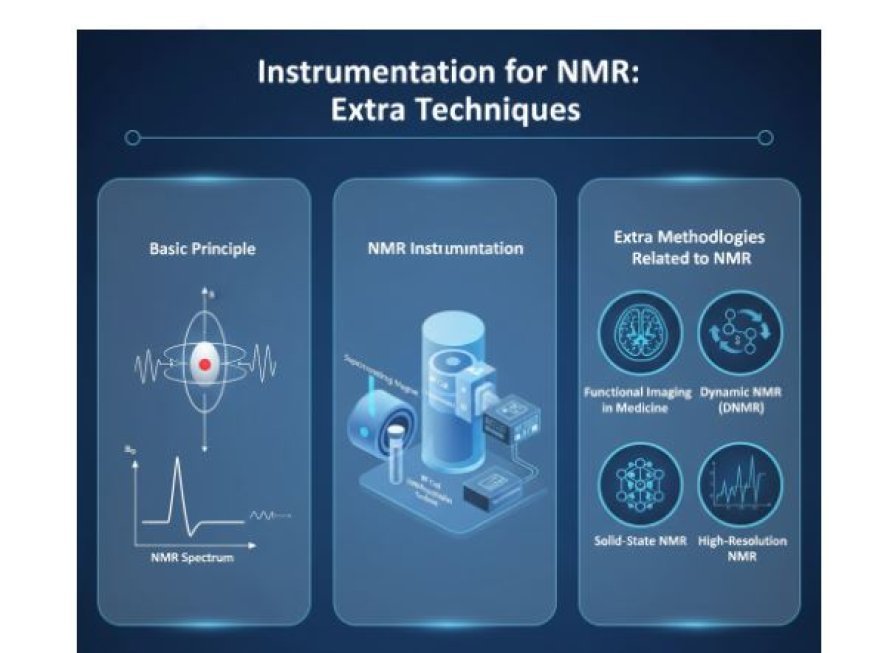
Instrumentation for NMR: Extra Techniques
Introduction
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a strong way to study the properties of atomic nuclei in physics, chemistry, and health.
- It helps scientists figure out how molecules are put together and how they move.
(NMR) Basic Principle
1.1 How NMR Works
- NMR is based on the idea that some atomic nuclei have a trait known as "spin."
- They line up with or against a strong magnetic field when placed in it.
- They can absorb radiofrequency radiation and transition to a higher energy state when exposed to it.
- This property makes NMR useful in many scientific fields.
1.2 Why It Matters
- NMR is useful because it provides information about:
- Chemical composition of substances
- Molecular interactions
- Molecular motion
- It plays a vital role in chemistry, where understanding molecular structures is key to developing new drugs and materials.
2. NMR Instrumentation
- NMR instruments consist of several main components that work together to carry out experiments.
2.1 Magnet
- The magnet is the core of an NMR machine.
- It creates a strong magnetic field that aligns the spins of atoms in a sample.
- Higher field strength results in better clarity and sensitivity of the spectra.
2.2 Radiofrequency (RF) Transmitter
- This component generates radio waves to excite the aligned nuclei.
- The frequency of these waves is precisely tuned to match the Larmor frequency of the nucleus being studied.
2.3 RF Receiver
- When excited nuclei relax back to their original energy state, they emit radio waves.
- These signals are detected by the RF receiver and converted into analyzable data.
2.4 Spectrometer
- The spectrometer processes the received signals and converts them into spectra (graphs showing the frequency of emitted radio waves).
- Scientists analyze these spectra to determine molecular structures and interactions.
3. Extra Methodologies Related to NMR
- Several advanced techniques are used alongside NMR to enhance its effectiveness.
3.1 Functional Imaging in Medicine
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a widely used medical imaging technique based on NMR.
- MRI provides detailed images of organs and tissues without using harmful radiation.
- It helps in diagnosing brain disorders, tumors, and cardiovascular diseases.
3.2 Dynamic NMR (DNMR)
- DNMR studies molecular motion and fast chemical reactions.
- By varying temperature or pressure, scientists can observe:
- Conformational changes in biomolecules
- Reaction mechanisms and energy barriers
- This technique helps in understanding protein folding and enzyme activities.
3.3 Solid-State NMR
- Unlike traditional NMR, which works best in liquid samples, solid-state NMR is designed for solid materials.
- Applications include:
-
- Studying polymers, catalysts, and advanced materials
- Analyzing protein structures in membranes
3.4 High-Resolution NMR
- Uses high-field magnets and advanced data processing to improve spectrum resolution.
- Important in:
- Pharmaceutical research (drug interactions)
- Structural biology (protein-ligand binding studies)
4. Applications of NMR Techniques
NMR has applications across chemistry, biochemistry, materials science, and medicine.
4.1 In Chemistry
- NMR is widely used to determine organic molecular structures.
- Helps in:
- Identifying functional groups
- Understanding molecular connectivity
- Verifying reaction steps in synthesis
4.2 In Biochemistry
- NMR helps study biological molecules like proteins, DNA, and enzymes.
- It aids in:
- Drug discovery by analyzing biomolecular interactions
- Understanding biochemical pathways
4.3 In Material Science
- NMR is used to analyze polymers, catalysts, nanomaterials, and battery components.
- Helps in optimizing materials for industrial and technological advancements.
4.4 In Medicine
- Beyond MRI, NMR helps in:
- Studying metabolism for disease diagnosis
- Analyzing blood and tissue samples for biomarker identification
- Investigating drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics
Conclusion
- NMR is an indispensable tool in scientific research and medical applications.
- With its advanced techniques and high precision, it provides critical insights into molecular structures, dynamics, and interactions.
- From drug discovery to material science, NMR continues to be a key driver of innovation and discovery.
IMAGE SOURCE (THUMBNAIL)
What's Your Reaction?