BOSE-EINSTEIN STATISTICS
Bose-Einstein statistics: Particles clumping up, defying classical expectations.
Bose-Einstein statistics
- In a quantum world, Bose-Einstein statistics explain how similar particles behave. It is a branch of statistical physics.
- It is named for Albert Einstein and Satyendra Nath Bose, who came up with the idea in the early 1920s.
- Bose-Einstein statistics are based on the idea that similar particles can't be told apart and that one particle's occupancy of a certain energy state doesn't stop another particle from filling that same energy state.
- In Bose-Einstein statistics, particles are thought to follow the Bose-Einstein distribution.
- This is a probability distribution that tells you how likely it is that you will find a particle in a certain energy state.
- How things are spread out depends on the system's temperature and chemical potential.
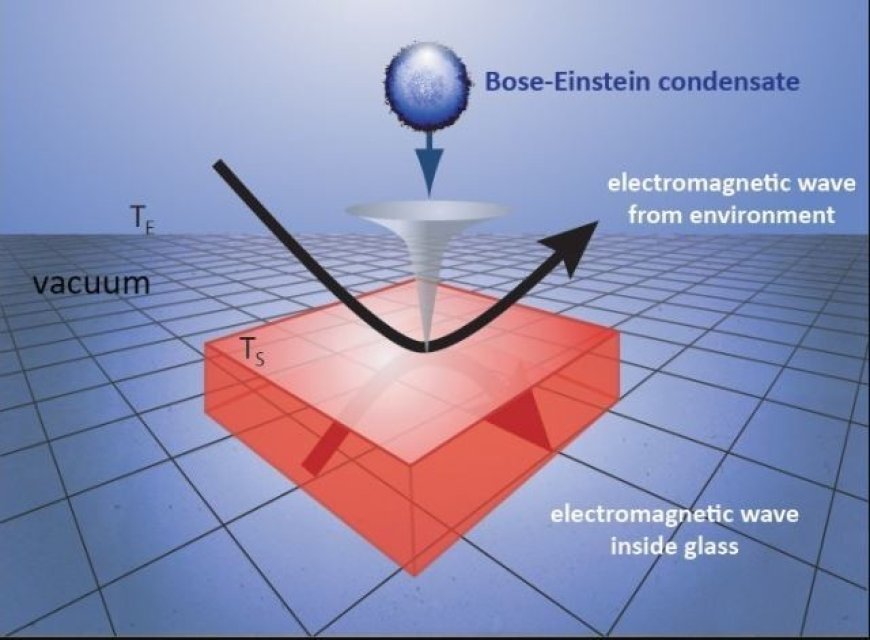
- According to Bose-Einstein statistics, a lot of particles will be in the lowest energy state when the temperature is low. This will cause a Bose-Einstein condensate to form.
Applications and limitations of Bose-Einstein statistics
- Bose-Einstein statistics are used in a lot of different areas of physics and engineering.
- It is used to study black holes, figure out how quarks and gluons behave in the quark-gluon plasma, and make lasers and masers.
- However, Bose-Einstein statistics has some flaws, especially when it comes to explaining how fermions, which are particles with half-integer spin, behave.
- Some ions, like electrons and protons, follow Fermi-Dirac statistics, which say that they can't be in the same energy state.
What's Your Reaction?