DIFFERENT BRANCHES OF THERMODYNAMICS
Thermodynamics branches: unraveling energy flow (Classical), reactions & spontaneity (Chemical), & the big picture (Statistical).
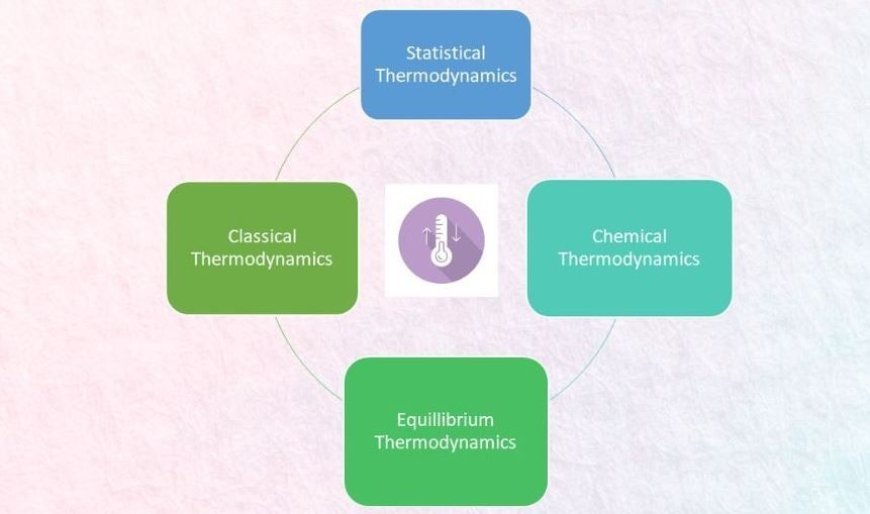
Different branches of thermodynamics
The study of thermodynamics can be broken down into the following groups:
- Classical Thermodynamics
- Chemical thermodynamics
- Equilibrium thermodynamics
- Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics
Classical thermodynamics
- In classical thermodynamics, the behaviour of matter is looked at on a large scale.
- People use units like temperature and pressure to figure out the properties and make predictions about the properties of the matter that is doing the process.
Statistical Thermodynamics
- During the late 1800s and early 1900s, atomic and molecular theories were developed.
- These theories led to the creation of statistical mechanics, which is also called statistical thermodynamics.
- It added a way to understand how tiny particles interact with each other or quantum mechanical states to classical thermodynamics.
- Classical thermodynamics is explained in this area by showing how statistics, classical physics, and quantum theory work at the microscopic level.
- To do this, it links the large-scale, tiny properties of things that people can see to the small-scale, macroscopic properties of individual atoms and molecules.
Chemical Thermodynamics
- As per the rules of thermodynamics, chemical thermodynamics is the study of how energy affects chemical processes or changes in state.
- The main goal of chemistry and thermodynamics is to find out how spontaneous a certain change is.
Equilibrium Thermodynamics
- Equilibrium thermodynamics is the study of how things in a system or substance can change from one thermodynamic equilibrium state to another.
- A state of balance called "thermodynamic equilibrium" means that all large-scale motions are zero. This means that for the simplest systems or things, their heavy qualities are all the same and their pressures are not affected by their edges.
- In an equilibrium state, there are no unbalanced potentials or pushing forces between the system's large-scale parts.
Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics
- Non-equilibrium thermodynamics is the branch of thermodynamics that studies systems that are not in thermodynamic equilibrium.
- Most systems in nature are not in thermodynamic equilibrium because they are not in a steady state and matter and energy are constantly and irregularly moving into and out of other systems.
- We require more general concepts than what equilibrium thermodynamics covers in order to study the thermodynamics of non-equilibrium systems.
What's Your Reaction?