BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATE (B.E.C.)
Einstein condensate: Supercold matter where particles act as one.
BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATE (B.E.C.)
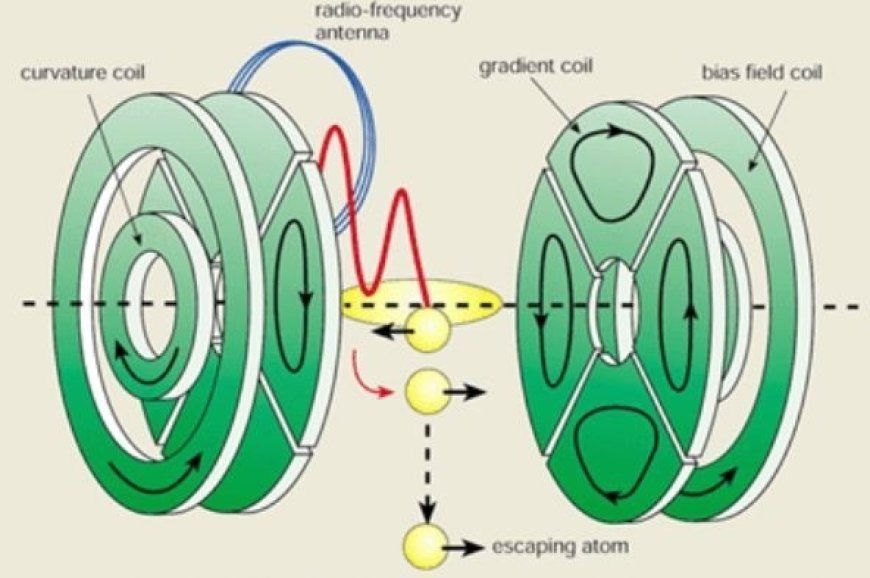
- Bose-Einstein condensate, or BEC, is a state of matter that happens when you cool a gas of bosons that is highly diluted to temperatures very close to zero.
- Around the same time, Albert Einstein and Satyendra Nath Bose came up with the first idea for BEC.
- When it gets that hot, the atoms don't move much relative to each other because they don't have much free energy to do so.
- After this, the atoms begin to group together and move to the same energy level. All of them physically blend into one another, and the group starts to act like a single atom.
- A Bose-Einstein condensate is another name for atoms that break down into a single quantum state.
- In a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), the atoms are the exact opposite of plasmas, which are very hot and energetic states of matter where electrons can move around easily. They are atoms that are very cold and not stirred.
- This is why B.E.C. stands for Bose-Einstein condensate; it means that the atom has broken down into a single quantum state.
What's Your Reaction?