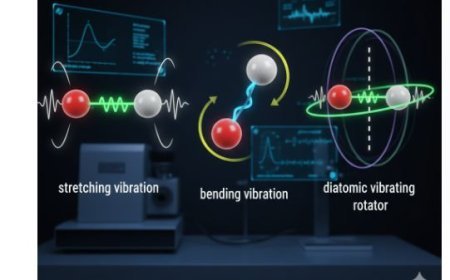
Symmetry and Conservation Laws
Symmetry and conservation laws are fundamental principles in physics that explain why certain quantities, like energy, momentum, and charge, remain constant. Through Noether’s Theorem, symmetries in nature correspond to conservation laws, helping scientists understand how the universe behaves consistently over time and space.
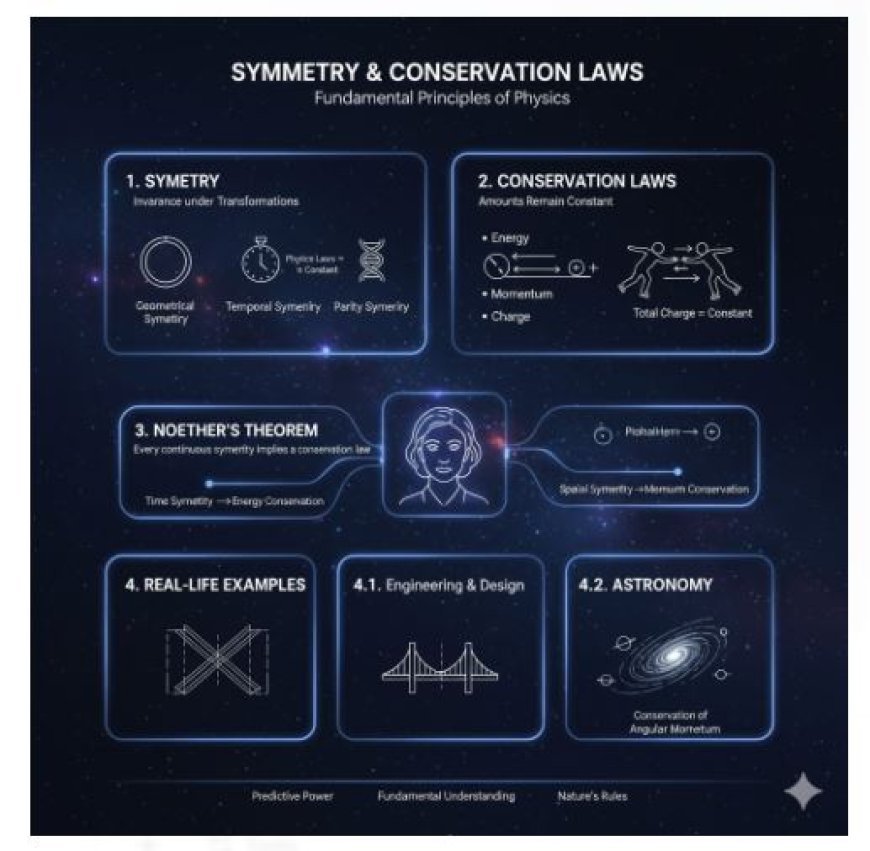
Symmetry and Conservation Laws
Physics has important ideas that help us understand the world. Symmetry and conservation rules are important for understanding how physical systems work.
1. Symmetry
Symmetry means that a system looks the same even after certain changes are made to it. In simple words, if you change something but it still looks or acts the same, we call it symmetrical.
Types of Symmetry
- Geometrical Symmetry: This is about shapes and their arrangements. A circle looks the same no matter how you look at it.
- Temporal Symmetry: This means that the rules of physics don't change over time. If you do an experiment today or tomorrow, the results should be the same.
- Parity Symmetry: This involves turning things around in space. For example, an object has parity symmetry if its mirror copy looks the same.
2. Conservation Laws
Conservation laws are basic rules in physics that say some amounts stay the same in closed systems. This means that these amounts can't be made or removed, only changed from one form to another.
Key Conservation Laws
- Conservation of Energy: The total energy in a closed system stays the same. Energy can change types (like from kinetic to potential), but the total amount stays the same.
- Conservation of Momentum: If there are no outside forces acting on it, the total momentum of a system stays the same.
- Example: When two ice dancers push against each other, the total motion stays the same before and after they push off.
- Conservation of Charge: The total electric charge in a closed system remains the same. Charge can move, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
3. How Symmetry Is Related to Conservation Laws
The link between symmetry and conservation rules is a basic concept in physics. This link is generally shown through Noether's Theorem, which is named after the mathematician Emmy Noether. The theory says that every time there is symmetry in physics, there is a related conservation rule.
Examples of This Link:
- Time Symmetry and Energy Conservation: The rules of physics do not change based on when an experiment is done, which means that energy must stay the same.
- Spatial Symmetry and Momentum Conservation: If the rules of physics are the same everywhere, then momentum is always preserved.
How It Works
When we see that certain patterns are present in a physical system, we can expect that a specific number will stay the same. This statement helps scientists predict how physical systems will behave using math.
4. Examples from Real Life
Knowing about symmetry and conservation rules is important in many areas of science and engineering. Here are some real-life effects:
- Physics of Collisions: In particle physics, when particles hit, they both keep the same total velocity and energy. This knowledge is important for understanding basic relationships in nature.
- Engineering and Design: Engineers use symmetry to create buildings that are both strong and attractive. This helps the structures resist forces coming from any direction.
- Astronomy: The conservation of angular momentum helps us understand how planets and stars are created and how they move in space.
What's Your Reaction?