Symmetric and Anti-Symmetric Wave Functions
In quantum mechanics, wave functions (Ψ) describe the complete quantum state of particles. When dealing with identical particles, understanding their symmetry properties becomes essential. A symmetric wave function remains unchanged when two particles are exchanged—this applies to bosons, which follow Bose-Einstein statistics and can share the same quantum state. Conversely, an anti-symmetric wave function changes sign upon exchange—characteristic of fermions, which obey Fermi-Dirac statistics and adhere to the Pauli Exclusion Principle. These symmetry principles not only determine atomic structure and bonding but also give rise to conservation laws and simplify complex quantum systems.
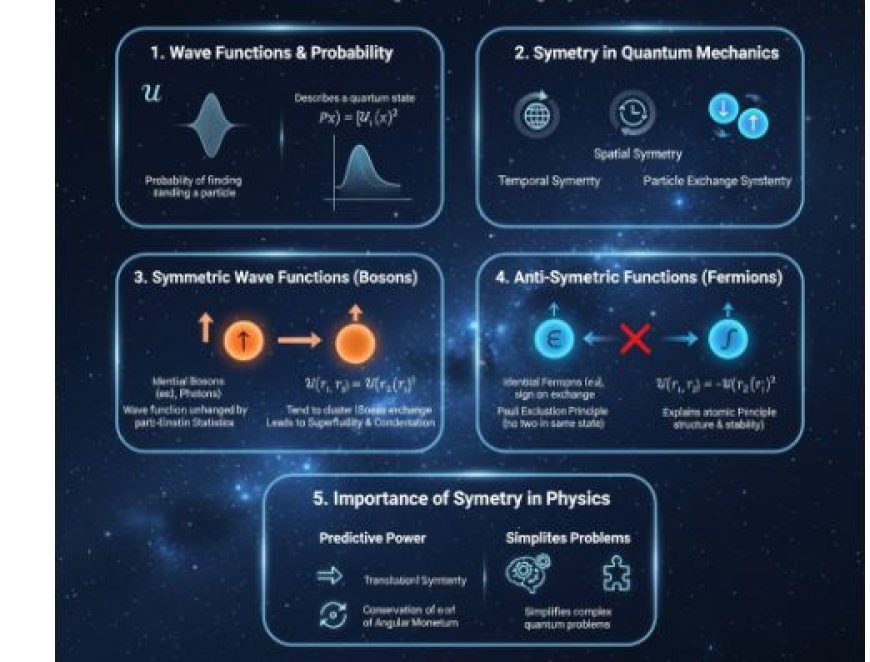
Symmetric and Anti-Symmetric Wave Functions
A wave function mathematically describes the quantum state of a system. It is represented by the Greek symbol Ψ (psi) and contains complete information about a particle or a system of particles. The probability of detecting a particle in a particular region of space is given by the square of the absolute value of the wave function:
This represents the probability density of finding the particle at a given location.
Importance of Wave Functions
- Quantum State Description: Provides a complete mathematical representation of a quantum system.
- Probability Interpretation: Helps calculate probabilities for physical attributes such as position and momentum.
Symmetry in Quantum Mechanics
Symmetry is a property of a system that remains unchanged under certain transformations, such as spatial translations, rotations, or particle exchanges.
Types of Symmetry
- Spatial Symmetry: A system exhibits spatial symmetry if it appears the same from different orientations.
- Temporal Symmetry: The laws of physics governing a system remain unchanged over time.
- Particle Exchange Symmetry: In multi-particle systems, this symmetry describes how wave functions behave when two identical particles are swapped.
Symmetric Wave Functions
A wave function is symmetric if it remains unchanged when two particles are exchanged:
Properties of Symmetric Wave Functions
- Identical bosons (e.g., photons, helium-4 atoms) require symmetric wave functions.
- This symmetry increases the probability of multiple bosons occupying the same quantum state due to their tendency to cluster together.
Implications
- Bose-Einstein Statistics: Describes how identical bosons are distributed among quantum states.
- Leads to phenomena like Bose-Einstein condensation, where particles group together in the lowest energy state.
Anti-Symmetric Wave Functions
A wave function is anti-symmetric if swapping two particles changes the sign of the function:
Properties of Anti-Symmetric Wave Functions
- Identical fermions (e.g., electrons, protons, neutrons) require anti-symmetric wave functions.
- This follows from the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that no two identical fermions can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously.
Implications
- Fermi-Dirac Statistics: Governs the distribution of fermions in quantum systems.
- Explains atomic structure, chemical bonding, and the stability of matter.
The Importance of Symmetry in Physics
1. Predictive Power
Symmetry principles allow physicists to predict system behavior. Many conservation laws arise due to symmetry:
- Translational symmetry → Conservation of momentum
- Rotational symmetry → Conservation of angular momentum
2. Simplifying Complex Problems
Recognizing symmetries helps solve challenging quantum mechanics problems. Identifying whether a system contains bosons or fermions allows physicists to derive physical properties without performing lengthy calculations.
What's Your Reaction?