REMOTE SENSING APPLICATIONS FOR LITHOLOGICAL AND STRUCTURAL MAPPING
Learn about the applications of remote sensing in lithological and structural mapping, including spectral analysis and image interpretation.
Remote Sensing Applications for Lithological and Structural Mapping
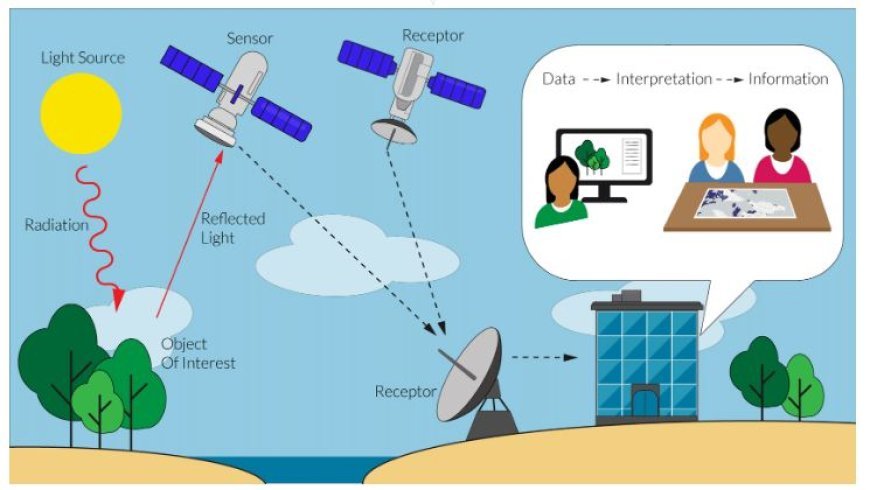
- Geological mapping relies on remote sensing, which is a quick and easy way to gather information over large areas.
- With this technology, monitors on platforms in the air or space can get information about the Earth's surface without touching it.
- Processing and analyzing the collected data can give us useful information about the lithology (rock types) and patterns in an area.
IMAGE SOURCE
- Lithological Mapping
- Spectral Analysis: In the electromagnetic range, different types of rocks have different spectral fingerprints. In other words, they reflect or absorb different colors of light in different ways.
- Satellite images can help identify and track different rock layers by looking at these changes in wavelength.
- Multispectral Imaging: Pictures taken by sensors that pick up a lot of different wavelengths let scientists look closely at the small changes in the wavelengths that different types of rocks have.
- This makes it easier to tell the difference between rocks that are sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic.
- Hyperspectral Imagery: This kind of imagery collects hundreds or even thousands of narrow spectral bands, which makes the spectral precision very high.
- It makes it possible to find certain minerals in rocks, even when the mineral abundance is low.
- Textural Analysis: You can also look at the surface structure of rocks, which is affected by their make-up and how they have been weathered.
- The information gathered from space can show patterns like cracks, bedding planes, and erosional features that help figure out the different types of rock.
- Radar Data: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data can go through clouds and plants to get useful information about the structure and roughness of rocks on the surface, which can be used for lithological mapping.
- Structural Mapping
- Lineament Analysis: Lineaments are straight lines on the surface of the Earth that often show natural structures like faults, fractures, and wrinkles.
- Remote sensing data can tell these features apart from the nearby land because their color, texture, or shape is different.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): DEMs made from stereo images or LiDAR data show differences in the land's surface, showing small changes in height that could mean the presence of lineaments.
- Image Processing Techniques: Edge recognition and image filtering are two techniques that can make lineaments easier to see, which makes them easier to identify and describe.
- Geomorphological analysis looks at how landscapes change over time to figure out what structures are underneath. Data from remote sensing can help find and map:
- Fault Scarps and Fault-Line Scarps: These landforms often show that there are large faults nearby.
Differential rise or deflation creates structural domes and basins, which show that folds and anticlines are below. - Patterns of Drainage: Structures below can have a big effect on the direction and shape of drainage systems. It is possible to figure out what these patterns mean by mapping them with data from remote sensing.
3. Applications in various fields
- For mineral prospecting, remote sensing is a common way to find potential places that need more research.
- Exploring geothermal areas: tracking areas with high heat flow and changed rocks using remote sensing data can help find places that might have geothermal potential.
- Exploring for Oil and Gas: Remote sensing helps map possible source rocks, storage rocks, and traps, which makes exploring for oil and gas easier.
- Monitoring the Environment: Remote sensing helps keep an eye on natural disasters like floods, earthquakes, and volcanic outbursts.
- Hydrogeological Studies: Data from remote sensing can help us understand how groundwater is distributed and what the properties of aquifers are.
- The Benefits of Using Remote Sensing for Geological Mapping
- Coverage: Remote sensing makes it easy to quickly collect data over large areas, giving a full picture of the rocks and minerals.
- Cost-effectiveness: Remote sensing is a cheaper way to map geological features than standard studies done on the ground.
- Repeatability: Data from remote sensing can be collected over and over again, which makes it possible to keep an eye on changes and processes in the earth's crust.
- Safety: With remote sensing, surveyors do not have to go to dangerous or hard-to-reach places in person, which keeps them safe.
What's Your Reaction?