Nuclear Forces
Learn about nuclear forces, the strongest forces in nature that bind protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Explore strong and weak forces, quark interactions, binding energy, and their role in nuclear stability and applications.

Nuclear Forces
Nuclear forces, or strong forces, are the attractions between protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. These forces are essential for maintaining the stability of matter and holding it together.
1. Main Features
Nuclear forces work over very short distances, typically around a femtometer (10⁻¹⁵ meters).
- The strongest of all fundamental forces: They are more powerful than electromagnetic forces, gravitational forces, and weak nuclear forces.
- Medium range: While very strong, their effect weakens rapidly over longer distances.
2. Parts of the Nucleus
To understand nuclear forces, it is important to know the components of an atomic nucleus:
a. Protons
- Positively charged particles found in the center of an atom.
- The number of protons determines the atomic number and the element.
b. Neutrons
- Neutral particles present in the nucleus.
- Neutrons increase the nucleus’s mass and help maintain stability.
3. Types of Nuclear Forces
Nuclear forces can be classified into two main types:
a. Strong Nuclear Force
- The primary force that holds protons and neutrons together.
- It functions by exchanging particles called mesons, primarily pions.
b. Weak Nuclear Force
- The weak force does not play a major role in binding the nucleus, but it causes nuclear decay (e.g., beta decay).
- It enables protons to change into neutrons, and vice versa.
4. The Role of Quarks
Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; they are made up of quarks, which are bound together by a fundamental force called the strong force (also known as Quantum Chromodynamics, QCD).
a. Quark Interaction
- Quarks inside protons and neutrons interact by exchanging particles called gluons.
- The strong force between quarks ensures the stability of protons and neutrons.
5. Binding Energy
Binding energy is the energy that holds the nucleus together.
a. Definition
- It is the energy required to separate a nucleus into its individual protons and neutrons.
b. Importance
- A higher binding energy means a more stable nucleus.
- It explains why some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive and decay over time.
c. Mass-Energy Equivalence
- Einstein’s famous equation E = mc² shows that mass can be converted into energy.
- The missing mass in a nucleus (when compared to the sum of its individual nucleons) is transformed into binding energy.
6. Effects of Nuclear Forces
Nuclear forces influence many fields, including:
a. Nuclear Energy
- Understanding nuclear forces is crucial for utilizing nuclear energy in fission and fusion reactions.
b. Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation therapy uses nuclear forces to treat cancer and other medical conditions.
c. Astrophysics
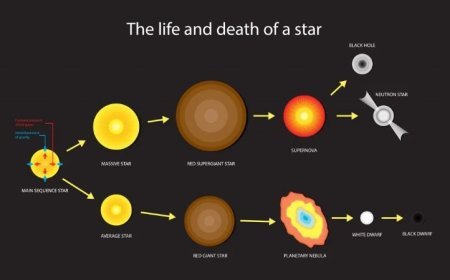
- Studying nuclear forces helps scientists understand stellar processes, such as fusion in stars and element formation during supernova explosions.
IMAGE SOURCE (THUMBNAIL)
What's Your Reaction?