LINEAR AND SYMMETRIC TOP MOLECULES
Learn about linear and symmetric top molecules, their structure, characteristics, examples, and importance in spectroscopy, materials science, and chemical reactions.
LINEAR AND SYMMETRIC TOP MOLECULES
- Molecules are the fundamental components of our surroundings, including air and food.
- In physics, molecules can be classified into two main types: linear molecules and symmetric top molecules.
- Linear molecules play a key role in studying molecular motion and spectroscopy.
1. Basics of Molecular Shapes
The shape and structure of molecules help in categorizing them into different groups. The way atoms are arranged in a molecule significantly impacts its properties and behavior.
A. Molecular Shapes
- Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
- Different Shapes: Molecules can have various structures such as linear, bent, tetrahedral, trigonal planar, and more, depending on the number of atoms and their bonding.
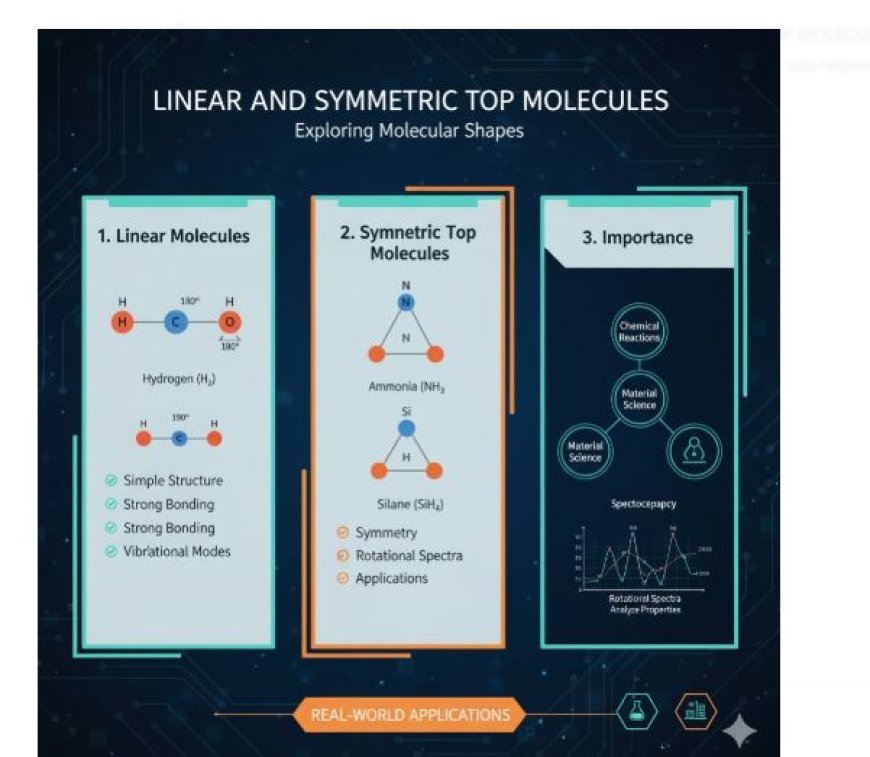
2. Linear Molecules
A. Definition
- Linear molecules have atoms arranged in a straight line.
- The bond angles in a linear molecule are 180 degrees.
Examples:
- Diatomic Molecules:
- Hydrogen (H₂), Oxygen (O₂), and Nitrogen (N₂).
- These consist of two atoms connected in a straight line.
- Polyatomic Molecules:
- Acetylene (C₂H₂) and Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) are examples of multi-atom linear molecules.
B. Characteristics
- Simple Structure: Linear molecules generally have simpler arrangements than other molecular shapes.
- Strong Bonding: The straight-line arrangement allows for strong bonds, making these molecules stable.
- Vibrational Modes: Linear molecules stretch and contract in specific ways when energy is applied, influencing their spectroscopic properties.
3. Symmetric Top Molecules
A. Definition
- Symmetric top molecules belong to a class of polyatomic molecules with three rotational planes and two equal moments of inertia.
- This symmetry affects how these molecules behave in different physical conditions.
Examples:
- Ammonia (NH₃): Though it has a trigonal pyramidal shape, it is considered a symmetric top because of its rotational properties.
- Silane (SiH₄): A classic example of a symmetric top molecule due to its even mass distribution.
B. Characteristics
- Symmetry: These molecules have highly symmetrical structures, influencing their rotational behavior.
- Rotational Spectra:
- Their symmetry results in complex rotational spectra, which help scientists understand molecular energy levels.
- Applications:
- Symmetric top molecules are crucial in spectroscopy, which studies how molecules absorb and emit light.
4. Importance of Understanding Molecular Shapes
Studying linear and symmetric top molecules is essential for multiple scientific disciplines.
A. Real-World Applications
- Chemical Reactions: Understanding molecular shape helps predict reaction behavior.
- Material Science: Molecular structure knowledge helps in designing new materials with specific properties.
B. Theoretical Models
- Molecular Dynamics: Studying these molecules helps develop models that predict how chemicals behave under different conditions, which is crucial for environmental science and medicine.
C. Spectroscopy
- Analytical Techniques: Spectroscopic methods rely on molecular shapes to identify substances and analyze their properties.
What's Your Reaction?