THERMODYNAMIC POTENTIALS
Thermodynamic Potentials: Shortcuts to predict work and equilibrium in a system.
Thermodynamic Potentials
- Thermodynamic potentials are numbers that show how much energy is stored in a system.
- Potentials are a way to measure how much energy moves in a system from its starting point to its ending point.
- Depending on the limits of the system, like temperature and pressure, different potentials are used.
- Thermodynamic potentials are quantities that capture the energy state of a system.
- Different potentials are relevant depending on the system's constraints, like temperature and pressure.
- Each potential tells us something different about the energy transfer within the system.
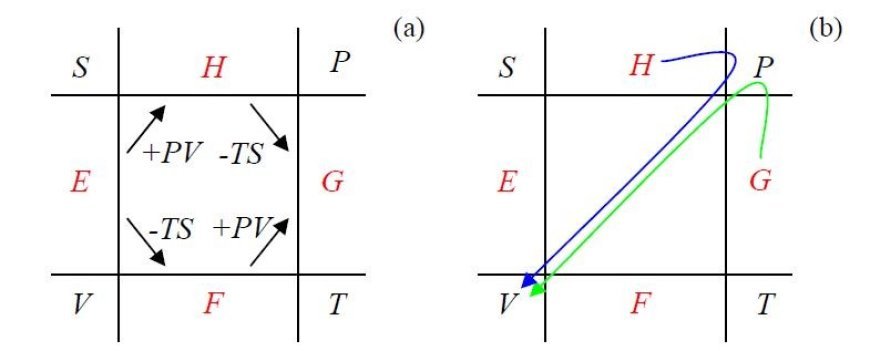
Here is a list of different types of thermodynamic potentials and their formulas:
Internal Energy
Helmholtz free energy F = U - TS
Enthalpy H = U + PV
Gibbs Free Power G = TS - U + PV
- The list of potentials and their formulas is also accurate.
- Internal energy (U) represents the total energy contained within the system.
- Helmholtz free energy (F) tells us the capacity for work at constant temperature and volume.
- Enthalpy (H) describes the energy available for work at constant pressure.
- Gibbs free energy (G) indicates the spontaneous direction of change in a system at a constant temperature and pressure.
What's Your Reaction?