SCHMITT TRIGGER
A Schmitt trigger is an electronic circuit that acts like a decision-maker for analog signals
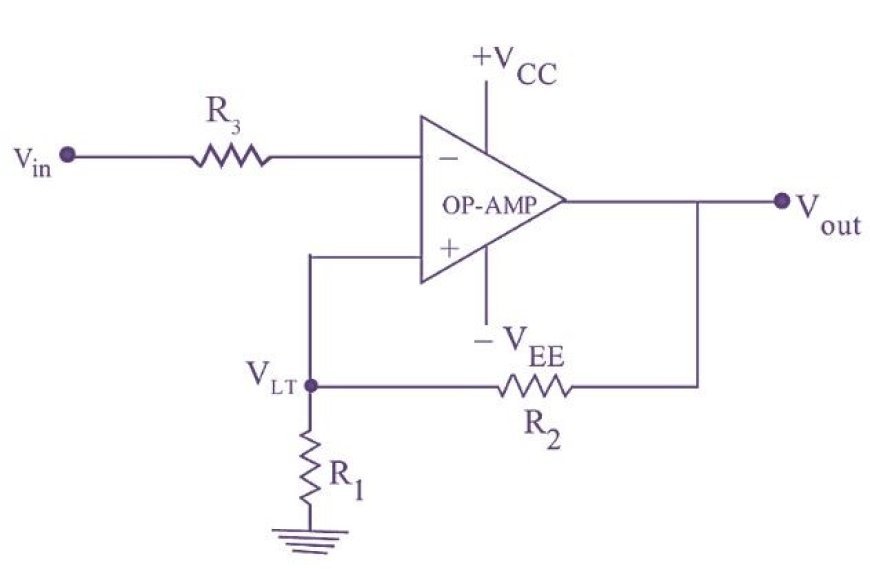
SCHMITT TRIGGER
- The idea of a Schmitt trigger comes from positive feedback.
- Any active circuit or device can be made to work like a Schmitt trigger by adding positive feedback so that the loop gain is higher than one.
- Someone lowers the active device's output voltage by a certain amount and sends it back to the input as positive feedback. This adds the input signal to the lowered output voltage.
- With higher and lower input voltage cutoff values, this makes hysteresis happen. This is because most buffers, inverters, and comparators only use one cutoff number.
- The output changes state whenever the input pattern goes above or below this level, in either way.
Mechanism of the Schmitt Trigger
- On the output, a signal that is noisy or has a slow pattern would show up as a string of noise waves.
- A Schmitt trigger fixes this. When the input voltage passes a threshold and changes the state of the output, the threshold changes as well. This means that the input voltage has to move farther in the opposite direction for the state to change again.
- On the other hand, noise or interference on the input would not show up on the output unless its amplitude was bigger than the difference between the two threshold numbers.
- You can tun any analog signal, like audio signals or sinusoidal patterns, into a set of ON-OFF pulses with smooth, quick edge changes.
- To make a Schmitt trigger circuit, the positive feedback can be set up in three different ways.
Advantages of the Schmitt trigger
- This is why Schmitt triggers are useful in any kind of high-speed data exchange system that processes digital signals in some way.
- In reality, they do two things: they get rid of noise and interference on data lines so that the data flow rate stays high, and they change a random analog waveform into an ON-OFF digital waveform with smooth, fast edge transitions. This is better than filters, which can get rid of noise but greatly slow down data rates because they have a limited capacity.
- Also, when a slow input waveform is used, normal filters can't give you a nice, clean digital output with fast edge changes.
Here are some more details about these two benefits of Schmitt triggers:
Sources of Noisy Signals
- Noise and crosstalk are big problems in digital systems because they get worse as lines get longer and data rates need to go up.
- Some popular ways to cut down on noise are to use shielded connections, twisted wires, match impedances, and lower output impedance.
- Even though these methods may help lower noise, there will still be some noise on an input line, which could cause a circuit to send out messages that aren't needed.
- A lot of the buffers, inverters, and comparators that are used in digital circuits only accept one cutoff value. In other words, the output changes state whenever the input pattern goes above or below this level, in either way.
- Random noise signals that cross this point more than once on an input will show up as a series of pulses on the output. On the other hand, a waveform with slow edge changes could show up on the output as a set of noise spikes that oscillate.
- A filter is sometimes used to get rid of this extra noise, like in an RC network.
- It does slow down the fastest data rate, though, when this kind of blocker is in the way of the data.
- A filter keeps out noise, but it also keeps out digital data with a high frequency.
What's Your Reaction?