SCANNING SYSTEMS AND DETECTORS
Understand the scanning systems and detectors used in remote sensing, including their principles, applications, and limitations.
Scanning Systems and Detectors
An overview of Remote Sensing Technology
- Remote sensing is a crucial area of research that improves our comprehension of the Earth.
- Geospatial data acquisition encompasses the gathering of information on the Earth's surface using a range of advanced methods and technology.
- The scanning systems and detectors are essential components of this technology, since they are responsible for collecting and analyzing remote sensing data.
Scanning systems
- Scanning systems are sophisticated equipment specifically engineered to gather data from the Earth's surface by taking photographs from various perspectives.
- Function: These systems play a crucial role in producing detailed maps and photographs of land and sea features, vegetation, and urban environments.
Classification of Scanning Systems
Passive Scanning systems:
- The working principle of passive scanning systems is to identify natural radiation, such sunlight, that is reflected off the surface of the Earth.
- Example: Optical sensors designed to detect and record sunlight that is reflected off different surface characteristics.
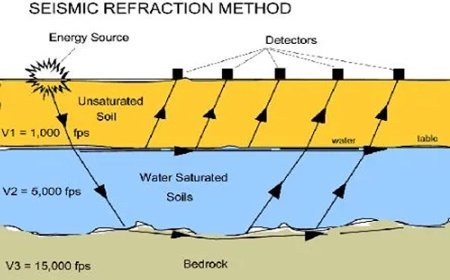
Active scanning systems
- Active scanning systems operate by emitting their own signals, such as radar waves or laser pulses, and then analyzing the reflected signal to collect information about the surface.
- Lidar, also known as Light Detection and Ranging, employs laser beams to accurately determine distances and map surface topography.
Benefits of Scanning Systems
- High Resolution: Possessing the ability to generate intricate visuals and data with exceptional accuracy.
- Comprehensive Scope: Capable of effectively capturing high-resolution photos of the Earth's surface on a vast scale.
- Versatility: Applicable in several domains, such as agriculture, urban development, and environmental monitoring.
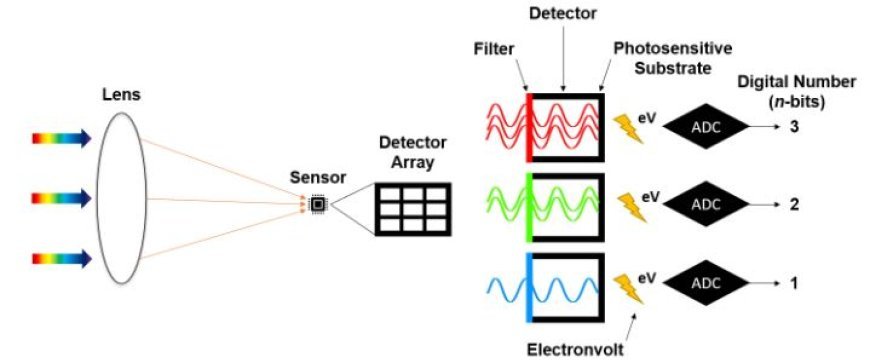
Detectors
- Detectors are sensors designed to accept signals from scanning systems and transform them into data that can be acted upon.
- Function: They play a crucial role in deciphering the data collected by scanning devices, making it easier to analyze remote sensing data.
Types of Detectors
- Photodetectors have the function of converting light into electrical signals, which may then be analyzed further.
- Usage: Typically employed in optical remote sensing systems to record fluctuations in light.
Radiometers
- Purpose: Quantify the magnitude of electromagnetic radiation.
- Purpose: Valuable for evaluating the thermal properties of the Earth's surface.
Radar Detectors: Purpose: Detect and capture radar waves that bounce back from the Earth's surface. - Purpose: Utilized in the process of active remote sensing to collect data on surface characteristics.
Importance of Detectors
- Superior detectors significantly improve the quality and precision of the obtained data.
- Precision: They guarantee dependable measurements that are crucial for precise analysis.
- Specialization: Various detectors are customized for specialized purposes, such as evaluating climatic conditions or addressing emergency situations.
Integration of Scanning Systems and Detectors
- Scanning systems have the task of acquiring Earth's surface data, while detectors play a vital role in analyzing and transforming this data into significant information.
- For example, a satellite outfitted with an optical scanning system may obtain photographs of a forest.
- The detector subsequently examines the reflected light to evaluate the condition and thickness of the forest.
Real-world uses
- Environmental Monitoring is a method employed to monitor and observe alterations in the environment, such as deforestation, wildfires, and pollution.
- Urban Planning involves the use of comprehensive mapping data to aid in the planning of municipal infrastructure and land use.
- Agriculture: Assists in assessing the condition of crops and predicting agricultural production.
What's Your Reaction?