REVERSING THERMOMETER AND BATHYTHERMOGRAPH
Reversing thermometers: Simple & reliable. Bathythermographs: Modern & detailed. Both measure ocean depths and temperatures.
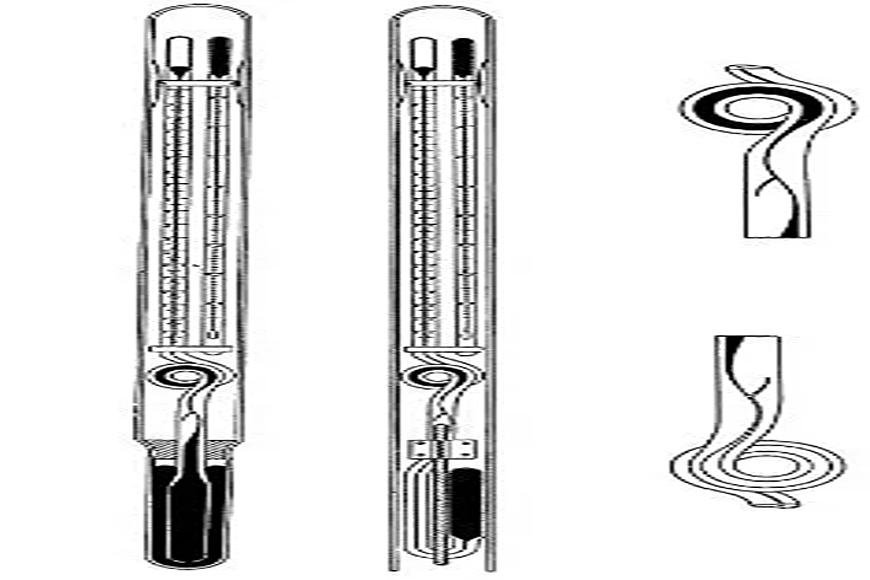
REVERSING THERMOMETER
- A reversing thermometer, unlike most traditional mercury thermometers, may record a temperature to be seen later.
- If the thermometer is turned upside down, the current temperature is shown until it is turned upright. This was the main tool that oceanographers used to measure water temperatures below the ocean's surface from roughly 1900 until 1970.
- It consists of a typical bulb attached to a capillary with a constriction such that the mercury column breaks off in a predictable way upon reversal.
- The mercury flows down the capillary into a smaller bulb that is graded to read temperature.
- If the thermometer is warmed and the mercury expands over the break-off point, a 360° turn in a temporarily expanded piece of the capillary acts as a trap to restrict further addition of mercury.
- Because of their remote-reading capabilities, reversing thermometers are ideal for measuring subsea temperature as a function of pressure.
- In this application, both protected and unprotected thermometers are employed, with each equipped with an auxiliary thermometer.
- In Nansen bottles, they are usually used in pairs.
- They are often read to 0.01°C and, following adequate changes, their readings are regarded as reliable to 0.02°C.
BATHYTHERMOGRAPH
- The bathythermograph, or BT, is a device that holds a temperature sensor and a transducer to measure variations in water temperature vs. depth down to roughly 285 meters (935 ft).
- A tiny winch onboard the ship lowers the BT into the water, where it plunges almost freely through the water while recording pressure and temperature changes on a coated glass slide.
- While dropping the instrument, the wire is paid out until it reaches a specified depth, at which point a brake is activated and the BT is brought back to the surface.
- Temperature data can be connected with the depth at which they are taken since pressure is a function of depth ( Pascal's law).
What's Your Reaction?