USES OF PALEONTOLOGICAL DATA IN VARIOUS FIELDS OF GEOLOGY
Discover the diverse applications of paleontological data in fields like geology, biology, and environmental science.
Uses of Paleontological Data in Various Fields of Geology
- Paleontological data obtained via the study of fossils is important in many disciplines of geology.
- Here are some important applications of paleontological data in various geological disciplines:
- Stratigraphy Fossils, especially index fossils (short-lived but widely dispersed species), aid in the correlation of rock strata across diverse geographical areas. This enables geologists to identify analogous layers and determine the relative ages of rock formations.
- Palaeontologists can date rock formations by detecting and dating fossils within sedimentary strata, allowing them to construct a geological timeline.
2. Paleoenvironmental reconstruction
- Reconstructing Past Habitats: Fossils reveal information about past climates and habitats.
- For example, the existence of plant fossils can indicate historical climatic conditions, such as a tropical rainforest or an arid desert.
- Understanding Ecosystems: Researching the plants and animals that coexisted can aid in the reconstruction of ancient ecosystems, shedding light on how past living forms interacted with their surroundings.
3. Paleo-climatology
- Climate Change Research: Fossil evidence can aid in reconstructing previous climates and understanding historical climate change.
- For example, analysing tree ring patterns and ice cores, as well as fossil material, can help us comprehend historical climatic conditions.
- Carbon Cycle Insights: Fossil records give information on past amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, which aids research into the Earth's carbon cycle and historical climatic shifts.
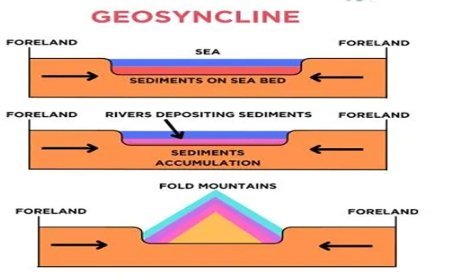
4. Tectonic and Plate Movements
- Plate Reconstruction: Fossils of species that were formerly widespread but are now isolated by enormous distances reveal information on ancient plate movements and continental drift.
- Paleogeographic Mapping: Fossil distributions let geologists recreate the placement of continents in the past, allowing them to map the Earth's ancient geography and better comprehend plate tectonics.
5. Hydrocarbon Exploration Source Rock Identification
- Fossils in sedimentary rocks indicate previous settings conducive to organic material buildup, making them suitable source rocks for hydrocarbons like oil and natural gas.
- Fossils help locate and characterise reservoir rocks (where oil and gas concentrate) and seal rocks (which trap hydrocarbons), both of which are crucial for effective exploration and extraction.
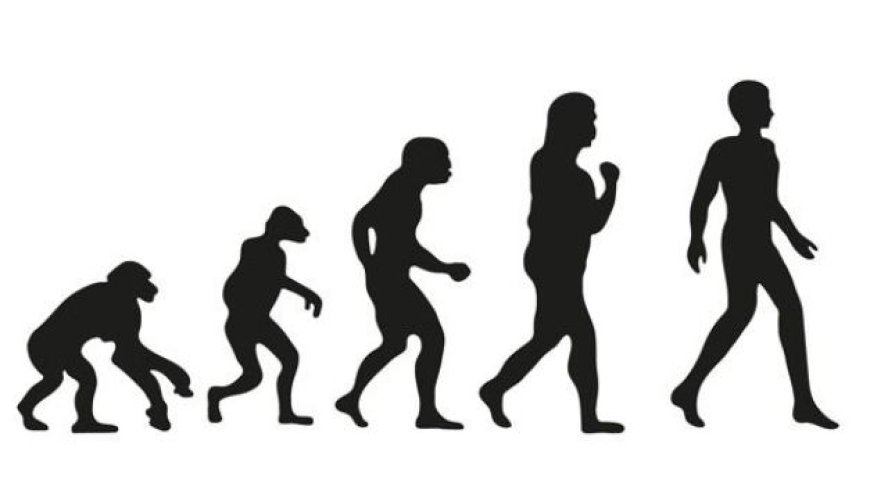
6. Evolutionary studies
- Understanding Evolutionary Processes: Fossils give direct evidence of evolutionary changes across time, allowing scientists to analyse the genesis and extinction of species.
- Phylogenetic links: Fossils aid in the reconstruction of evolutionary links between extinct and existing species, therefore improving our understanding of the tree of life.
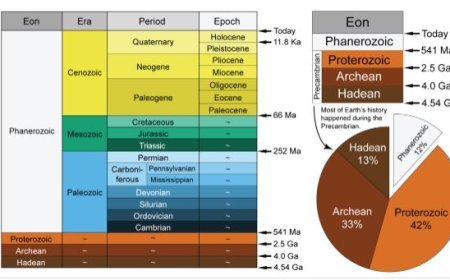
7. Geochronology
- Fossils with documented evolutionary histories are employed to date geological events, including mass extinctions.
- Temporal Calibration: Fossil data is used to calibrate geological time scales, giving a foundation for understanding the timing and duration of geological eras.
8. Paleo-biogeography
- Tracking Species Distribution: Fossils give information on how species moved and adapted to diverse environments across time.
- This aids in comprehending previous biogeographic patterns and how geographical barriers impacted species distributions.
- Fossil records reflect previous biodiversity and how it evolved throughout time, which helps us comprehend historical life forms and their distribution.
9. Educational and Public Engagement
- Museums employ fossils to teach visitors about Earth's history, evolution, and prehistoric life.
- Scientific Outreach: Paleontological data is utilised in outreach projects to educate students and the general public about geology and evolution.
What's Your Reaction?