PRECAMBRIAN FOSSILS STROMATOLITES AND EDICARAN FAUNA
Discover the earliest evidence of life on Earth, including Precambrian fossils, stromatolites, and Ediacaran fauna.
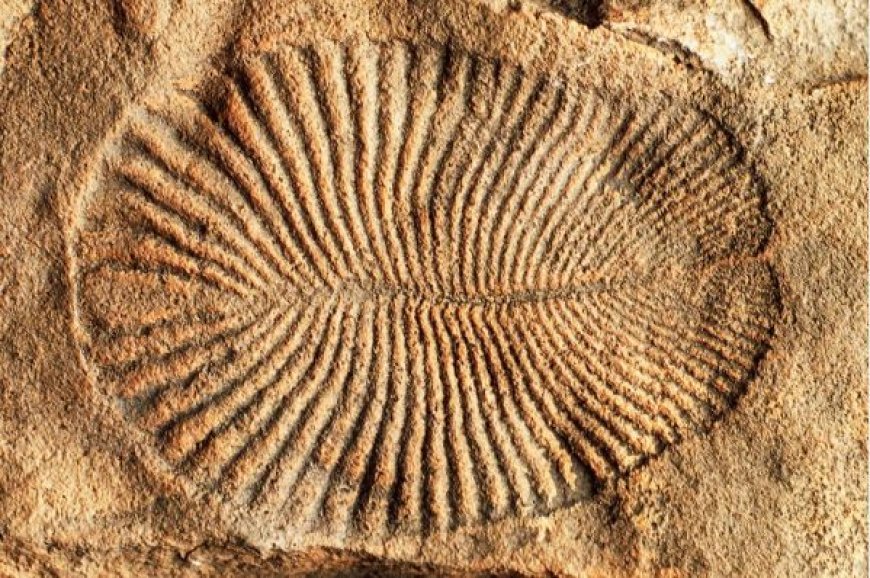

Stromatolites and Ediacaran fauna are examples of precambrian fossils
- The Precambrian era, which runs from the birth of the Earth around 4.6 billion years ago to the beginning of the Cambrian period around 541 million years ago, accounts for the great bulk of Earth's history.
- During this epoch, life evolved significantly, with Precambrian fossils giving crucial insights into early biological development.
- Stromatolites and Ediacaran fauna are some of the most remarkable fossils from this time period.
1) Stromatolites
- Stromatolites: Layered sedimentary formations formed by microorganisms, especially cyanobacteria (blue-green algae).
- They are among Earth's oldest known fossils, dating back more than 3.5 billion years.
- Stromatolites grow in shallow seas where microbial mats catch and hold sediment.
2. Stromatolite structure
- Stromatolites feature different layered structures, which may be found in fossilized forms.
- Lamellae are thin layers that reflect sediment and microbial development patterns over time.
- Cyanobacterial mats are live layers formed by cyanobacteria that photosynthesise and produce oxygen.
- Sediment Trapping: As cyanobacteria expand, they trap sediments, resulting in the layered look.
3. The Significance of Stromatolites
- Stromatolites are crucial in comprehending the Earth's early ecosystem.
- Ecosystem indicators reveal prehistoric sea conditions and ecosystem types.
- Cyanobacteria's photosynthetic activities led to the Great Oxidation Event, which altered the
- Earth's atmosphere and enabled the emergence of complex life.
- Stromatolites are essential for investigating ancient biogeochemical cycles and microbiological activity.
2. Ediacaran fauna
1. What is the Ediacaran fauna?
- The Ediacaran fauna is a collection of soft-bodied, multicellular creatures that flourished between 635 and 541 million years ago.
- These animals are regarded as some of the oldest sophisticated living forms on Earth, and their fossils give critical information on the development of life prior to the Cambrian explosion.
2. Characteristics of the Ediacaran fauna
- Ediacaran fossils are distinctive and diversified, with a variety of shapes and forms.
- The morphology of these organisms varies, with some resembling current jellyfish, worms, or corals, and others unclassified.
- The majority of Ediacaran species were soft-bodied, making fossilization unusual. They are commonly found in fine-grained sedimentary rocks.
3. Major Groups of Ediacaran Fauna
- The Ediacaran biota can be divided into various categories:
- Dickinsonia and Charniodiscus show leaf-like structures.
- Kimberella, an intriguing disk-shaped animal, is thought to be a forerunner of molluscs.
- Holdfast organisms were anchored to the bottom and resembled current seaweeds.
4. The Significance of Ediacaran Fauna
- The Ediacaran biota is important for a variety of reasons, including:
- Evolutionary Transition: They reflect a significant shift from simple to complex living forms, indicating the advent of multicellularity.
- Studying Ediacaran fauna provides insights into ancient ecosystems, including predator-prey interactions and ecological niches.
- Precursors of Cambrian Life: The Ediacaran species helped to fuel the Cambrian period's explosion of biological variety.
What's Your Reaction?