EVOLUTION OF INVERTEBRATES ACROSS GEOLOGICAL AGES
EVOLUTION OF INVERTEBRATES ACROSS GEOLOGICAL AGES : Explore the evolution of vertebrates through geologic time, from ancient fish to modern humans.
Evolution of Invertebrates across Geological Ages
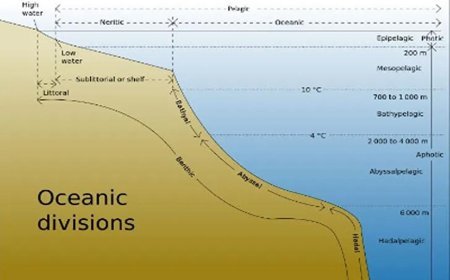
- For billions of years, the dominating life form on Earth has been invertebrates, or creatures without a backbone.
- Their evolutionary path from the Precambrian to the present demonstrates life's tremendous variety and resilience.
Precambrian: The Origin of Invertebrate Life
- The Ediacaran Period saw the creation of the first complex multicellular animals, including intriguing species like jellyfish and flatworms.
- The appearance of soft-bodied organisms: These early invertebrates lacked hard components, laying the groundwork for later evolutionary developments.
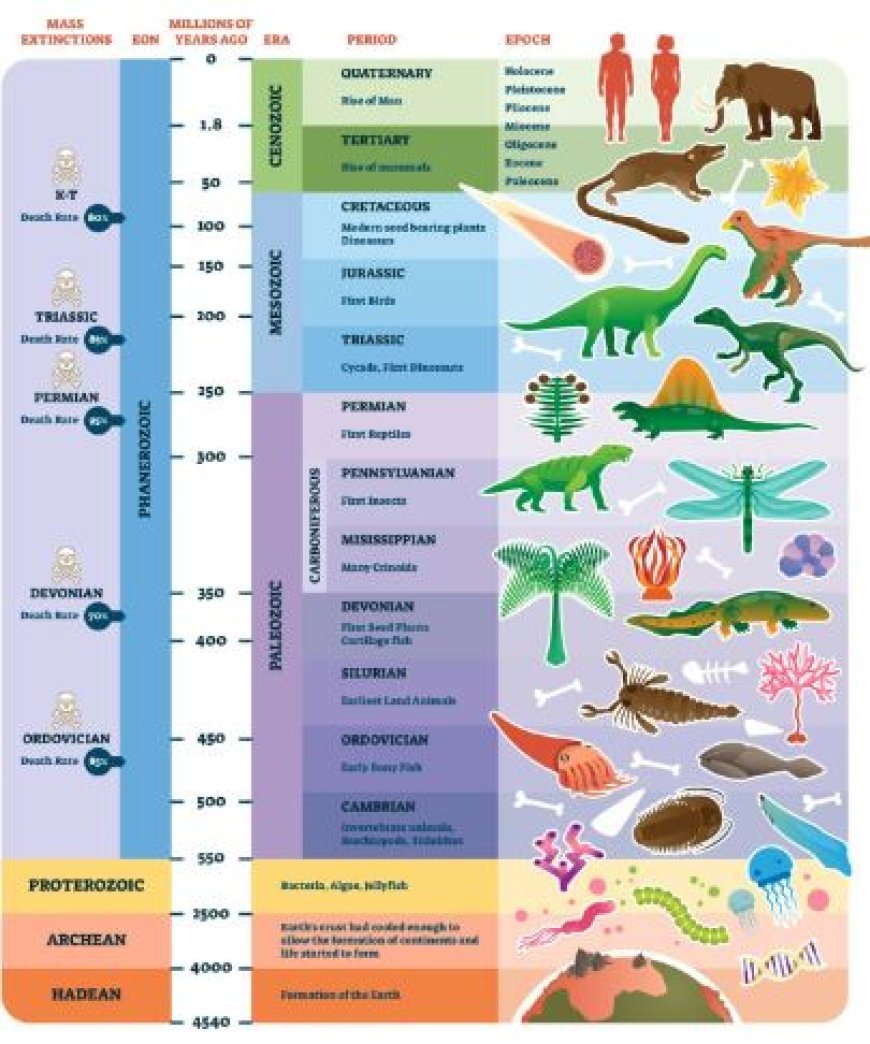
Paleozoic Era: Invertebrate Explosion
- Cambrian era: A era of rapid diversification known as the "Cambrian Explosion," characterized by the advent of a diverse range of invertebrates with hard parts, including trilobites, brachiopods, and mollusks.
- The Ordovician Period saw continued diversity of marine invertebrates, including the appearance of graptolites and corals.
- Silurian Period: Early arthropods colonized the land, marking an important milestone in the development of terrestrial life.
- Devonian period: This was the "Age of Fishes," but it was also a time of great animal growth, with early insects and different kinds of ammonoids appearing.
- During the Carboniferous Period, insects dominated and huge coral reefs formed.
Permian era: A mass extinction event at the end of the era resulted in a major decrease in invertebrate species.
Mesozoic Era: Recovery and Adaptation
- The Triassic Period saw the recovery from the Permian extinction, with the emergence of new invertebrate taxa such as ammonoids and bivalves.
- The Jurassic Period saw continued diversity of marine invertebrates, including the development of modern-looking bivalves and gastropods.
- During the Cretaceous Period, plankton flourished and different invertebrate groups such as ammonites and belemnites evolved.
Cenozoic Era: Modern Invertebrate assemblages
- During the Paleogene Period, mollusks and echinoderms continued to diversify, giving rise to modern-looking groupings.
- The Neogene Period saw the emergence of coral reefs and the spread of benthic animals, ushering in the present invertebrate community.
Evolutionary Trends
- Development of hard parts: Shells, exoskeletons, and internal skeletons offered protection and support, resulting in greater variety and complexity.
- Adaptive radiation describes periods of rapid diversity in response to new ecological possibilities or environmental changes.
- Extinction events: Mass extinctions affected invertebrate evolution, with survivors often experiencing adaptive radiations.
- Coevolution: Invertebrates' interactions with other creatures, such as plants and predators, fueled evolutionary creativity.
What's Your Reaction?