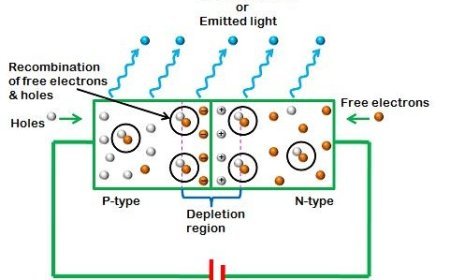
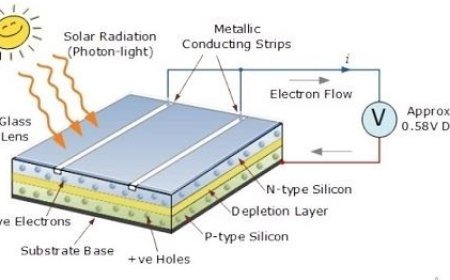
Nuclear Forces and Their Importance
Nuclear forces are the invisible glue that binds protons and neutrons within the atomic nucleus. This article explores the strength, range, and nature of nuclear forces, including spin dependence, charge independence, and the exchange of pions and gluons. Learn how these forces shape nuclear stability, enable fusion and fission, and power applications in energy and medicine. A deep dive into the structure of matter, the nucleus model, and the strong interaction that governs atomic behavior.
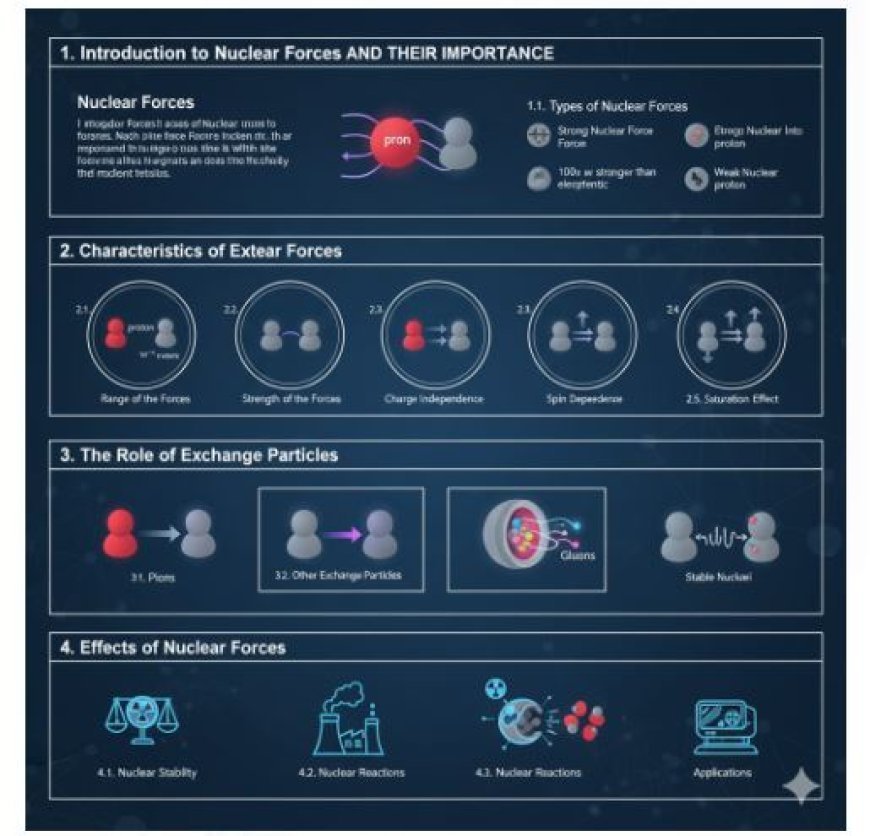
Nuclear Forces and Their Importance
1. Introduction to Nuclear Forces
Nuclear forces are the interactions that keep protons and neutrons, which are called nucleons, together in the center of an atom. These forces are much stronger than gravity or electricity, but they only work over very short distances.
1.1. Types of Nuclear Forces
- Strong Nuclear Force: This is the main force that keeps nucleons held together. It is responsible for overcoming the electromagnetic repulsion between protons, as they all carry a positive charge.
- Weak Nuclear Force: This force is important in processes such as beta decay, where neutrons can change into protons and vice versa.
2. Characteristics of Nuclear Forces
To understand nuclear forces, there are a few important points to consider:
2.1. Range of the Forces
Nuclear forces work well only at very small distances, about one femtometer (10⁻¹⁵ meters). After this point, their impact quickly decreases.
2.2. Strength of the Forces
- Very Strong: The strong nuclear force is the most powerful of all the basic forces. It is about 100 times more powerful than electromagnetic forces at the nuclear level.
2.3. Charge Independence
- Charge Independence: The forces within a nucleus do not rely on whether the nucleons have a positive or neutral charge. This means that the way protons and neutrons interact is similar to how protons interact with each other or how neutrons do, but there are some variations.
2.4. Spin Dependence
- Spin Interaction: Nuclear forces depend on the spin of nucleons, which influences how they interact with each other. For example, two nucleons with their spins in the same direction can pull each other more strongly than when their spins are in opposite directions.
2.5. Saturation Effect
- Saturation: Nuclear forces reach a maximum, so each nucleon only strongly reacts with a few other nucleons. This helps explain why atomic nuclei are stable.
3. The Role of Exchange Particles
Nuclear forces are handled by particles called exchange particles.
3.1. Pions
- Pions: These are particles that help transmit the strong nuclear force. When nucleons get close to each other, they swap pions, which creates a strong attraction between them.
3.2. Other Exchange Particles
- Gluons: Quarks inside nucleons are joined together by gluons. Gluons are particles that carry the strong force, which is a fundamental interaction.
4. Effects of Nuclear Forces
Nuclear forces have important effects in different areas of physics:
4.1. Nuclear Stability
- Stability of Nuclei: An atomic nucleus is stable when the strong nuclear forces and electromagnetic forces are balanced. Stable isotopes are balanced in a way that keeps them from breaking apart.
4.2. Nuclear Reactions
- Nuclear Fusion and Fission: It’s important to understand nuclear forces when talking about fusion (when nuclei join together) and fission (when nuclei split apart), as both processes produce a large amount of energy.
4.3. Applications
- Nuclear Energy and Medicine: Understanding nuclear forces is important in nuclear physics. This knowledge helps in generating energy in nuclear plants and using radiation in medical imaging and treatment.
What's Your Reaction?