MOSFET REGIONS OF OPERATIONS
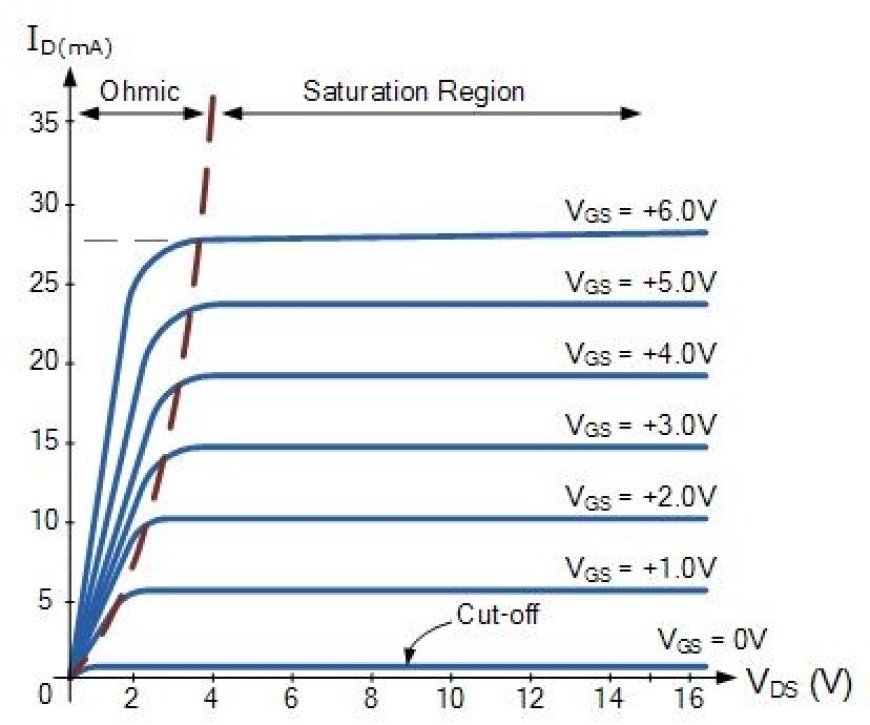
MOSFETs operate in three regions: cut-off (minimal current), triode (current increases with voltage), and saturation (current reaches a constant value).
MOSFET Regions of Operation
Regarding the broadest sense, this gadget mostly works in three areas, which are listed below:
Cut-off-Region
- If the current flow stops in the cut-off area, the gadget is turned off, and no electricity flows through it.
- In this case, the device works as a basic switch, which is how they are used when they need to work as electrical switches.
Saturation region
- When the devices are in the saturation area, the current flowing from the drain to the source stays the same, even though the voltage across the drain to the source is rising. This only takes place once, when the voltage rises above the pinch-off voltage value across the drain to the source wire.
- In this case, the device acts as a closed switch, with a lot of current flowing from the drain to the source ports. This means that the saturation region is chosen when the devices are supposed to move.
Linear/Ohmic Region
- As the voltage across the drain-to-source path rises, so does the current across the drain-to-source terminal. This is called the linear or ohmic, area.
- Amplification is what the MOSFET devices do when they work in this straight area.
What's Your Reaction?