MEAN FREE PATH
Mean free path: The average distance a particle travels between collisions.
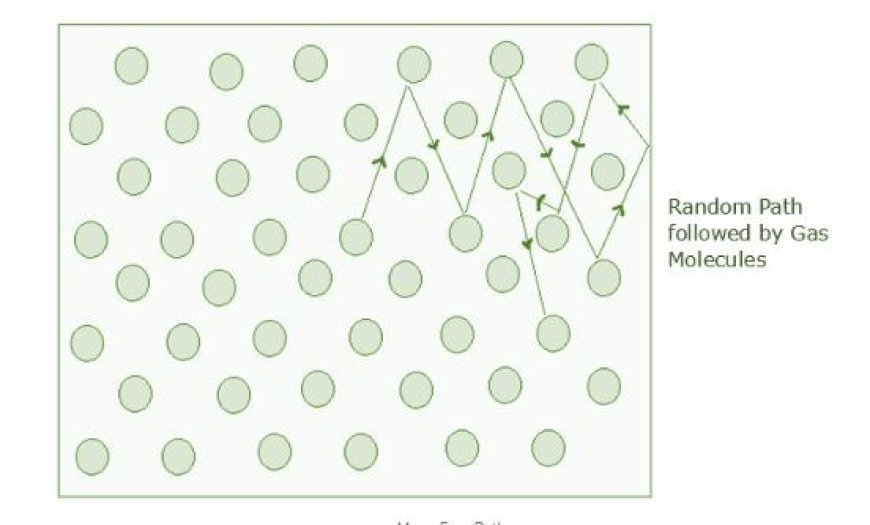
Mean Free Path
- This is the average distance a gas molecule travels without hitting anything.
In math, the mean free path can be shown as follows:
- Let's look at how a gas molecule moves inside an ideal gas.
- A normal molecule inside an ideal gas will quickly change its direction and speed when it hits other molecules of the same gas.
- Though the molecule will move in a straight path at a constant speed between collisions, this is true for all molecules in the gas.
- Though the molecule will move in a straight line at a steady speed in between hits, all molecules in the gas will move in this way.
- This random movement of gas molecules is hard to measure or explain, so we try to find its mean free path (λ).
- The average distance a molecule travels between collisions is called λ.
- We expect λ to change inversely with N/V, which is the number of molecules per unit volume or the density of molecules. This is because the more molecules there are, the more likely it is that they will collide with each other, which lowers the mean free path.
- λ would also change inversely with the diameter d of the molecules, since if the molecules were point masses, they would not move.
- Because we are looking at the cross-section of a circle and not the diameter itself, it should be proportional to π times the diameter square.
What's Your Reaction?