GEOMORPHOLOGY AND ITS TYPES
Geomorphology studies landforms (mountains, valleys, etc.) and how natural forces shape them (fluvial, glacial, etc.).

GEOMORPHOLOGY
- There are mountains, islands, lakes, rivers, glaciers, and other bodies of water in the oceans, as well as planets and moons in our solar system.
- The field of geomorphology helps us understand and respect these landscapes and landforms of all sizes.
- Geomorphologists often say that the different shapes and forms that make up the Earth's surface are beautiful to them. Imagine geomorphology as "the study of landscape" from this perspective.
- Geography is where geomorphology got its start, but it has grown into an important Earth Science area that helps us understand and solve many environmental issues.
- Scientists and historians who study geology, hydrology, engineering, oceanography, geographers, and people who study land use are using geomorphological ideas and methods more and more to solve issues.
RELEVANCE IN INDIA
- Plateaus, deserts, floodplains, lakes, deltas, and mountains are just a few of the landscapes that you can find in India. Also, India has the second-most people of any country in the world.
- The land is always being pushed to its limits so that people can have food and a place to live.
- This and human-caused climate change are speeding up and changing the geomorphic processes that are already in motion.
- This makes geomorphic dangers like landslides, floods, droughts, desertification, salinization, siltation, coastal and riverside erosion, landslides, melting glaciers, rising sea levels, falling groundwater levels, and more happen more often and with more force.
- Geomorphologists are very important for dealing with these trends and, if possible, turning them around. These are some of the most important and brand-new geomorphology topics.
Tectonic Geomorphology
- The main tenet of tectonic geomorphology is that tectonic processes interact with processes on the surface, such as weathering and erosion, to create the earth's structures, such as cracks and wrinkles.
- This tells us more about how the surface of the earth changes where tectonic plates are moving.
- You can trust records of past temperatures and paleoseismological data more now than ever before, thanks to new dates and geomatic methods.
- It has been very helpful to use these methods to find out how fast the crust moves and how old things in the scenery are.
Process Geomorphology
- Wind, moving water, and moving ice all change the Earth's surface.
- Things, people, and plants all do too. When these "drivers" of geomorphic change get power from the sun, they change places in their own unique ways and leave their mark.
- To figure out how to measure geomorphic systems, we need to look at the connection between processes and landforms.
- If you use logic and look at facts from the real world, the main goal of process geomorphology is to find mathematical models that can link energy, mass, and time.
- The main way that geomorphic risks are dealt with is based on the findings of these kinds of studies.
Palaeogeomorphology
- To fully understand how a geomorphic system works, you need to know how a place has changed over time.
- Paleoclimatological, palaeoecological, and historical records are often used to help with geomorphological studies. We can use proxy indicators, which are indirect types of data that can be used to rebuild paleolandscapes, to find out how changes in temperature and landforms from the past are linked.
- We can learn a lot about how areas change over time and space by using new geochemical methods, such as dating sediments and looking at the isotopic makeup of sediments and water.
- This is especially true when we compare this new knowledge to what we already know about the history of climate and tectonics.
- Building up places from a certain time period also helps history connect what people did in the past with natural events.
- It has been possible to figure out what the paleochannels were used for and how they worked in the past.
- People have been able to find new places to get water and placer reserves thanks to this.
Planetary Geomorphology
- Satellites, landers, and rovers in the solar system gather detailed information from the world's surfaces.
- This data tells us a lot of different things that help us figure out which geomorphic traits are still alive and which ones are not.
- Some of the features look a lot like features on Earth.
- This has led scientists from many fields, like chemistry and physics, to model them to try to figure out how they formed.
- We now know more about how the earth's surface works because of this.
- Different rates of erosion, the sizes of landforms, and geomorphic processes that require more in-depth study all contribute to problems in the challenging field of geomorphology.
Biogeomorphology and Environmental Geomorphology
- In biogeomorphology, different types of feedback, each with a different strength and value, connect the physical and biological parts of the world.
- Environmental management, on the other hand, is a social system with many levels that studies how people's actions change the shape of the earth's surface.
- A lot of current geomorphology research looks at how these changing biophysical links with human activity can help us guess how areas will respond to climate change and changes made by people.
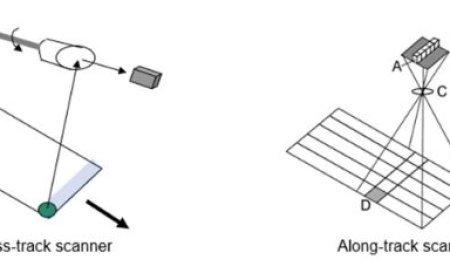
Geoinformatics and Modelling
- Geoinformatics is the study of how to use science and technology to gather and change geographic data so that it can be used to find useful information by analysing and showing it in different ways.
- This makes people smarter about what to do. There are now better remote sensing and navigation systems that allow geoinformatics to be used in more areas linked to geomorphology.
- Mathematical methods are being used more and more to find, study, explain, and describe geomorphological patterns and processes so that we can better understand the space and time aspects of the landscape.
What's Your Reaction?