EARTH DISASTER MANAGEMENT PLANNING
Learn about effective disaster management strategies for mitigating the impact of earthquakes, landslides, floods, and other earth-related disasters.
Disaster Management Planning
- In an era when we are constantly confronted with nature's relentless might, the significance of proper disaster management planning has never been more evident.
- Natural disasters—whether earthquakes, floods, landslides, tsunamis, or volcanic eruptions—pose serious threats to human lives, infrastructure, and the environment.
- As we work to reduce these hazards, the incorporation of geology into disaster management plans emerges as a vital aspect of protecting communities.
Understanding Geology's Implications
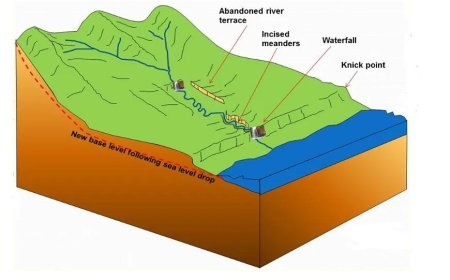
- Geology, or the study of the Earth's physical structure and composition, as well as its history and the processes that shape it, provides significant information about natural dangers.
- Understanding the geological characteristics and processes that define a place allows planners to foresee possible disasters and develop effective mitigation measures. Here are some of the ways geology may help with disaster management:
1. Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
- The first step in good disaster management is to recognize possible dangers.
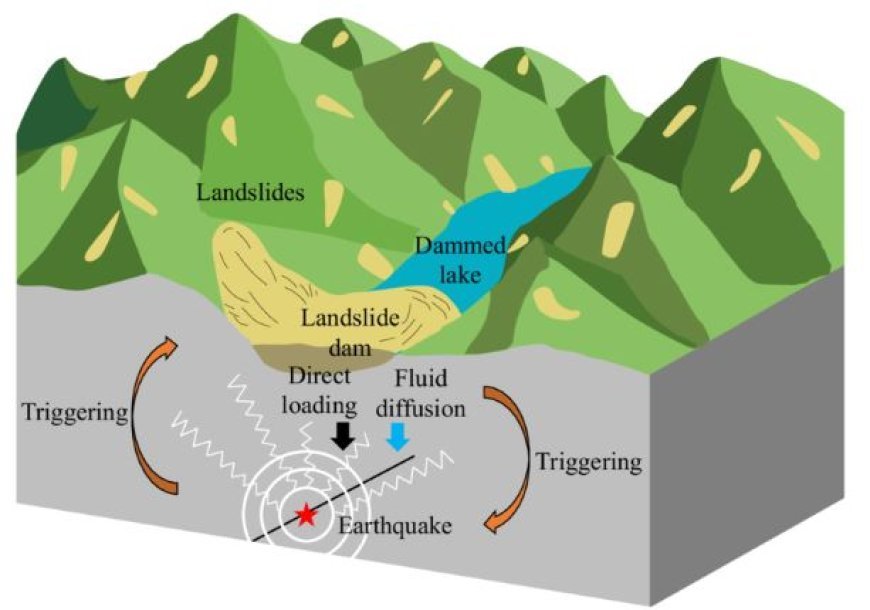
- Geological surveys give critical data on fault lines, soil types, and rock formations, allowing policymakers to better anticipate where and how disasters are likely to strike.
- For example, places near tectonic plate borders are more vulnerable to earthquakes, but areas with soft soil may experience greater flood hazards owing to anaerobic conditions.
- Geological data serves as the foundation for risk assessments, which are essentially extensive analyses of the probability and implications of various risks.
- Identifying high-risk locations allows communities to prioritize resources and develop preventative or preparedness plans tailored to their specific circumstances.
2. Land Use Planning and Zoning
- Geology influences land use planning, ensuring that settlements are designed in a resilient manner.
- Soil stability, slope angles, and drainage patterns should all be considered when deciding where to develop and locate infrastructure.
- For example, new buildings near recognized floodplains or on unstable slopes might worsen the effects of natural catastrophes.
- Incorporating geological data into zoning rules can help prevent hazardous buildings and encourage safe urban expansion.
3. Early Warning Systems
- Geologists play an important role in the creation of early warning systems for natural disasters like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- Scientists can discover trends that indicate an impending occurrence by researching previous geological activity, allowing people to plan and respond more efficiently.
- Monitoring seismic activity, for example, allows the government to warn the public about imminent earthquakes, reducing turmoil and saving lives.
4. Emergency Response and Recovery Plans
- Understanding geological elements helps create more efficient emergency response plans.
- For example, understanding the geography may help guide evacuation routes, ensuring that they are both safe and accessible during a crisis.
- Geology also has an influence on post-disaster recovery; locations with low soil stability may require longer recovery durations owing to probable landslides or infrastructure damage.
- Geological evaluations help communities comprehend the long-term alteration of landscapes following disasters.
- This understanding enables the creation of resilient rebuilding plans that take into account future threats rather than just repairing what has been harmed.
5. Education and Community Engagement
- Incorporating geology into disaster management plans highlights the value of community education.
- Local residents should be informed of the geological dangers in their area, including potential hazards and disaster response procedures.
- Knowledge fosters resilience, allowing societies to adjust to inevitable geological conditions and become proactive rather than reactive.
What's Your Reaction?